Page 40 - OR-1-3
P. 40
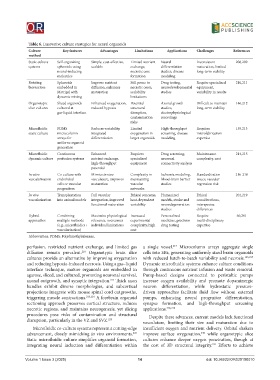
Table 6. Innovative culture strategies for neural organoids
Culture Key features Advantages Limitations Applications Challenges References
method
Static culture Self-organizing Simple, cost-effective, Limited nutrient Neural Inconsistent 208,209
systems spheroids using scalable exchange, differentiation maturation, limited
neural-inducing necrotic core studies, disease long-term viability
molecules formation modeling
Rotating Spheroids Improve nutrient Still prone to Drug testing, Require specialized 210,211
bioreactors embedded in diffusion, enhances necrotic cores, neurodevelopmental equipment,
Matrigel with maturation scalability studies variability in results
dynamic mixing limitations
Organotypic Sliced organoids Enhanced oxygenation, Potential Axonal growth Difficult to maintain 146,212
slice cultures cultured at reduced hypoxia structural studies, long-term viability
gas-liquid interface disruption, electrophysiological
contamination recordings
risks
Microfluidic PDMS Reduces variability, Limited High-throughput Requires 135,213
static culture microcolumn integrated oxygenation in screening, disease microfabrication
arrays for differentiation larger organoids modeling expertise
uniform organoid
generation
Microfluidic Continuous Enhanced Requires Drug screening, Maintenance 214,215
dynamic culture perfusion systems nutrient exchange, specialized neuronal complexity, cost
high-throughput equipment connectivity analysis
potential
In vitro Co-culture with Mimics in vivo Complexity in Ischemia modeling, Standardization 216-218
vascularization endothelial vasculature, improves maintaining blood-brain barrier issues, vascular
cells or vascular maturation vascular studies regression risk
progenitors networks
In vivo Transplantation Full vascular Ethical concerns, Humanized Ethical 201,219
vascularization into animal models integration, improved host-dependent models, stroke and considerations,
functional maturation variability neurodegeneration interspecies
studies differences
Hybrid Combining Maximize physiological Increased Personalized Require 60,201
approaches multiple methods relevance, overcomes experimental medicine, precision multi-disciplinary
(e.g., microfluidics+ individual limitations complexity, high drug testing expertise
vascularization) cost
Abbreviation: PDMS: Polydimethylsiloxane.
perfusion, restricted nutrient exchange, and limited gas a single vessel. Microcolumn arrays aggregate single
217
diffusion remain prevalent. Organotypic brain slice cells into EBs, generating uniformly sized brain organoids
210
cultures provide an alternative by improving oxygenation with reduced batch-to-batch variability and necrosis. 135,227
and reducing hypoxia-induced necrosis. Using a gas–liquid Dynamic microfluidic systems enhance culture conditions
interface technique, mature organoids are embedded in through continuous nutrient infusion and waste removal.
agarose, sliced, and cultured, promoting neuronal survival, Pump-based designs connected to peristaltic pumps
axonal outgrowth, and synaptic integration. Thick axon increase oxygen availability and promote dopaminergic
222
bundles exhibit diverse morphologies, and subcortical neuron differentiation, while hydrostatic pressure-
projections integrate with mouse spinal cord outgrowths, driven approaches facilitate fluid flow without external
triggering muscle contractions. 223,224 A forebrain organoid pumps, enhancing neural progenitor differentiation,
sectioning approach preserves cortical structure, reduces synapse formation, and high-throughput screening
necrotic regions, and maintains neurogenesis, yet slicing applications. 228,229
procedures pose risks of contamination and structural Despite these advances, current models lack functional
disruption, particularly in the VZ and SVZ. 225 vasculature, limiting their size and maturation due to
Microfluidic co-culture systems represent a cutting-edge insufficient oxygen and nutrient delivery. Orbital shakers
advancement, closely mimicking in vivo environments. improve surface oxygenation, while organotypic slice
230
226
Static microfluidic culture simplifies organoid formation, cultures enhance deeper oxygen penetration, though at
integrating neural induction and differentiation within the cost of 3D structural integrity. Efforts to achieve
231
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/OR025100010