Page 36 - OR-1-3
P. 36
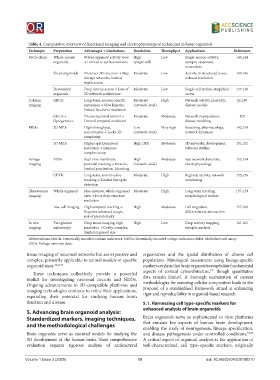
Table 4. Comparative overview of functional imaging and electrophysiological techniques in brain organoids
Technique Preparation Advantages → Limitations Resolution Throughput Applications References
Patch-clamp Whole-mount Whole-organoid activity view High Low Single-neuron activity, 143,144
organoids → Limited to surface neurons (single-cell) synaptic responses,
maturation
Sliced organoids Preserves 3D structure → May Moderate Low Activity in structured tissue, 145,146
disrupt networks, limited reduced resolution
depth access
Dissociated Deep neuron access → Loss of Moderate Low Single-cell studies, simplified 147,148
organoids 3D network architecture access
Calcium GECIs Long-term, neuron-specific Moderate High Network activity, plasticity, 62,149
imaging expression → Slow kinetics, (network-level) disease models
limited fast event resolution
GECIs + Precise neuronal control → Moderate Moderate Network manipulation, 129
Optogenetics Limited temporal resolution disease modeling
MEAs 2D MEA High-throughput, Low Very high Screening, pharmacology, 142,150
non-invasive → Lacks 3D (network-level) network dynamics
complexity
3D MEA Higher spatiotemporal High (3D) Moderate 3D networks, development, 151,152
resolution → Requires behavior studies
complex setup
Voltage VSDs Real-time membrane High Moderate Fast network dynamics, 153,154
imaging potential tracking → Invasive, (network-wide) electrophysiology
limited penetration, bleaching
GEVIs Long-term, non-invasive Moderate High Regional activity, network 155,156
tracking → Limited fast spike monitoring
detection
Fluorescence Whole organoid Non-invasive, whole-organoid Moderate High Long-term tracking, 157-159
imaging view → Poor deep structure morphological studies
resolution
Live-cell imaging High temporal tracking → High Moderate Cell migration, 157,160
Requires advanced setups, differentiation, interaction
risk of phototoxicity
In vivo Two-photon Deep tissue imaging, high High Low Deep activity mapping, 161,162
imaging microscopy resolution → Costly, complex, synaptic analysis
limited organoid size
Abbreviations: GECIs: Genetically encoded calcium indicators; GEVIs: Genetically encoded voltage indicators; MEA: Multielectrode array;
VSDs: Voltage-sensitive dyes.
tissue imaging of neuronal networks but are expensive and organization and the spatial distribution of diverse cell
complex, primarily applicable to animal models or specific populations. Histological assessments using lineage-specific
organoid sizes. 162,174 markers confirm that brain organoids recapitulate fundamental
175
These techniques collectively provide a powerful aspects of cortical cytoarchitecture, though quantitative
toolkit for investigating neuronal circuits and NDDs. data remain limited. A thorough examination of current
Ongoing advancements in 3D-compatible platforms and methodologies for assessing cellular composition leads to the
imaging technologies continue to refine their applications, proposal of a standardized framework aimed at enhancing
expanding their potential for studying human brain rigor and reproducibility in organoid-based research.
function and disease. 5.1. Harnessing cell type-specific markers for
enhanced analysis of brain organoids
5. Advancing brain organoid analysis:
Standardized markers, imaging techniques, Brain organoids serve as sophisticated in vitro platforms
and the methodological challenges that emulate key aspects of human brain development,
enabling the study of neurogenesis, lineage specification,
Brain organoids serve as essential models for studying the and disease pathogenesis under controlled conditions. 52,56
3D development of the human brain. Their comprehensive A critical aspect of organoid analysis is the application of
evaluation requires rigorous analysis of architectural well-characterized, cell type–specific markers, originally
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 10 doi: 10.36922/OR025100010