Page 33 - OR-1-3
P. 33
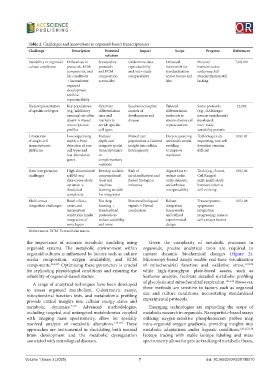
Table 2. Challenges and innovations in organoid-based transcriptomics
Challenge Description Potential Impact Scope Progress References
solution
Variability in organoid Differences in Standardize Undermine data Universal Protocol 7,60,101
culture conditions protocols, ECM protocols reproducibility framework for harmonization
components, and and ECM and inter-study standardization underway; full
lab conditions composition comparability across tissues and standardization still
→ Inconsistent across labs labs lacking
organoid
development
and low
reproducibility
Underrepresentation Key populations Optimize Lead to incomplete Tailored Some protocols 42,102
of specific cell types (e.g., inhibitory differentiation models of differentiation (e.g., GABAergic
neurons) are often cues and development and protocols to neuron enrichment)
absent → Biased markers to disease ensure diverse cell developed;
transcriptomic enrich specific representation inter-study
profiles cell types variability persists
Limitations Low sequencing Increase Missed rare Deep sequencing Technologies are 103,104
of single-cell depth → Poor depth and populations → Limited and multi-modal improving; rare cell
transcriptomic detection of rare integrate spatial insight into cellular profiling detection remains
platforms cell types and transcriptomics heterogeneity to improve difficult
low-abundance or resolution
genes complementary
methods
Data interpretation High-dimensional Develop scalable Risk of Algorithms to Tools (e.g., Seurat, 105,106
challenges scRNA-seq computational misclassification and reduce noise, Cell Ranger)
data+cross-study tools and flawed biological unify datasets, exist; multi-study
variation → machine inference and enhance harmonization is
Analytical learning models interpretability still evolving
complexity for integration
Multi-omics Batch effects, Use deep Distorted biological Robust Transcriptome– 107,108
integration challenges noise, and learning + signals → Flawed integration epigenome
inconsistent Standardized conclusions frameworks integration
conditions hinder protocols to and refined progressing; noise is
integration of reduce variability experimental still a major barrier
omic layers and noise design
Abbreviation: ECM: Extracellular matrix.
the importance of accurate metabolic modeling using Given the complexity of metabolic processes in
organoid systems. The metabolic environment within organoids, precise analytical tools are required to
organoid cultures is influenced by factors such as culture capture dynamic biochemical changes (Figure 2).
media composition, oxygen availability, and ECM Microscopy-based assays enable real-time visualization
components. 114,115 Optimizing these parameters is crucial of mitochondrial function and oxidative stress, 119,120
for replicating physiological conditions and ensuring the while high-throughput plate-based assays, such as
reliability of organoid-based studies. Seahorse analysis, facilitate detailed metabolic profiling
A range of analytical techniques have been developed of glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration. 121,122 However,
to assess organoid metabolism. Colorimetric assays, these methods are sensitive to factors such as organoid
mitochondrial function tests, and metabolomic profiling size and culture conditions, necessitating standardized
provide critical insights into cellular energy states and experimental protocols.
metabolic dynamics. 7,116 Advanced methodologies, Emerging technologies are expanding the scope of
including targeted and untargeted metabolomics coupled metabolic research in organoids. Nanoparticle-based assays
with imaging mass spectrometry, allow for spatially utilizing oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent probes map
resolved analysis of metabolic alterations. 117,118 These intra-organoid oxygen gradients, providing insights into
approaches are instrumental in elucidating both normal metabolic adaptations under hypoxic conditions. 120,123,124
brain development and the metabolic dysregulation Isotope tracing with stable isotope labeling and mass
associated with neurological diseases. spectrometry allows for precise tracking of metabolic fluxes,
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/OR025100010