Page 45 - TD-3-2
P. 45
Tumor Discovery PG of maxillary median gingiva in a pediatric patient
was eventually referred to our department for further mass with the right upper deciduous central incisor
examination and treatment. (Figure 4B and C). After resection, the healthy gingiva
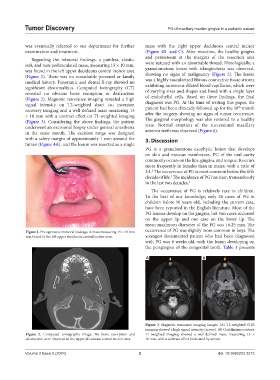
Regarding the intraoral findings, a painless, elastic, and periosteum at the margins of the resection area
soft, and non-pedunculated mass, measuring 15 × 10 mm, were sutured with an absorbable thread. Histologically, a
was found in the left upper deciduous central incisor area granulomatous lesion with telangiectasia was observed,
(Figure 1). There was no remarkable personal or family showing no signs of malignancy (Figure 5). The lesion
medical history. Panoramic and dental X-ray showed no was a highly vascularized fibrous connective tissue stroma
significant abnormalities. Computed tomography (CT) exhibiting numerous dilated blood capillaries, which were
revealed no obvious bone resorption or destruction of varying sizes and shapes and lined with a single layer
(Figure 2). Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a high of endothelial cells. Based on these findings, the final
signal intensity on T2-weighted short tau inversion diagnosis was PG. At the time of writing this paper, the
th
recovery imaging and a well-defined mass measuring 13 patient had been clinically followed up for the 18 month
× 10 mm with a contrast effect on T1-weighted imaging after the surgery, showing no signs of tumor recurrence.
(Figure 3). Considering the above findings, the patient The gingival morphology was also restored to a healthy
underwent an excisional biopsy under general anesthesia state. Normal eruption of the successional maxillary
in the same month. The excision range was designed anterior teeth was observed (Figure 6).
with a safety margin of approximately 1 mm around the 3. Discussion
tumor (Figure 4A), and the lesion was resected as a single
PG is a granulomatous exophytic lesion that develops
on skin and mucous membranes. PG of the oral cavity
commonly occurs on the lips, gingiva, and tongue. It occurs
more frequently in females than in males, with a ratio of
2:1. The occurrence of PG is most common before the fifth
2
decade of life. The incidence of PG has risen tremendously
3
in the last two decades. 2
The occurrence of PG is relatively rare in children.
To the best of our knowledge, only 26 cases of PG in
children below 10 years old, including the current case,
have been reported in the English literature. Most of the
PG lesions develop on the gingiva, but two cases occurred
on the upper lip and one case on the lower lip. The
mean maximum diameter of the PG was 16.25 mm. The
Figure 1. Pre-operative intraoral findings. A mass measuring 15 × 10 mm occurrence of PG was slightly more common in boys. The
was found in the left upper deciduous central incisor area. youngest documented patient who had been diagnosed
with PG was 8 weeks old, with the lesion developing on
the perigingiva of the congenital tooth. Table 1 presents
A B
Figure 3. Magnetic resonance imaging images. (A) T2-weighted STIR
imaging showed a high signal intensity (arrow). (B) Gadolinium contrast
Figure 2. Computed tomography image. No bone resorption and T1-weighted imaging showed a well-defined mass, measuring 13 ×
destruction were observed in the upper deciduous central incisor area. 10 mm, with a contrast effect (indicated by arrow).
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/td.2213