Page 71 - TD-3-3
P. 71
Tumor Discovery Pyroptosis-related genes in breast cancer progression
27
A present study are significantly associated with mitosis.
Thus, they may point to additional pathways for BC
progression. The down-regulation of RGS1 may be closely
related to DNA methylation-dependent silencing or
immune escape. The RGS1, a member of the G protein
signal transduction family, is an important tumor immune
C escape site. Due to RGS1 being down-regulated in this
28
analysis, a joint study of BC and immune pathways may be
carried out in the future.
The PSME2 might be a significant oncogene or tumor
suppressor gene for the prevention or early diagnosis
of BC. PSME2, which plays the role of an oncogene or
tumor suppressor gene through multiple pathways in
BC, endometrial cancer, and other malignant tumors,
is implicated in immunoproteasome assembly and is
B required for efficient antigen processing. In this study,
PSME2 was down-regulated in BC, indicating that the
diagnosis and recurrence of BC may be related to its
misregulation.
In the risk model, several genes related to BC have not
yet been extensively studied or have unclear pathways,
including PXDNL, ARMH1, and APOBEC3F. First,
up-regulated PXDNL, a member of the peroxidase gene
family, has been identified as a potential independent
prognostic biomarker for BC, and it appears to be
associated with reduced OS and recurrence-free survival
rates. Second, ARMH1, also known as C1orf228, has
29
been investigated in only three studies, with its relevance
primarily noted in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Unfortunately, its pathway in BC remains unclear. Finally,
APOBEC3D and APOBEC3F, which are pseudogenes, have
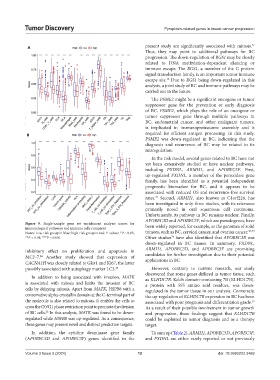
Figure 9. Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis scores for been widely reported, for example, as the genomes of solid
immunological pathways and immune cells compared
Notes: Low-risk group in blue; high-risk group in red; P-values: *P < 0.05; tumors, such as BC, cervical cancer, and ovarian cancer. 30-33
34
**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Other studies have also identified that APOBEC3B was
down-regulated in BC tissues. In summary, PXDNL,
inhibitory effect on proliferation and apoptosis in ARMH1, APOBEC3D, and APOBEC3F are promising
MCF-7. Another study showed that expression of candidates for further investigation due to their potential
24
applications in BC.
CACNA1H was closely related to Glut1 and Ki67, the latter
possibly associated with autophagy marker LC3. 25 However, contrary to current research, our study
discovered that some genes differed in tumor tissue, such
In addition to being associated with invasion, MATK as KLHDC7B. Kelch domain-containing 7B (KLHDC7B),
is associated with mitosis and limits the invasion of BC a protein with 595 amino acid residues, was down-
cells by delaying mitosis. Apart from MATK, HSPB8 with a regulated in the tumor tissue in our analysis. Conversely,
conservative alpha-crystallin domain at the C-terminal part of the up-regulation of KLHDC7B expression in BC has been
the molecule is also related to mitosis. It enables the cells to associated with poor prognosis and differentiation grade.
35
cross the G0/G1 phase restriction point to promote the division As a result of their possible involvement in tumor growth
26
of BC cells. In this analysis, MATK was found to be down- and progression, these findings suggest that KLHDC7B
regulated while HSPB8 was up-regulated. As a consequence, could be exploited in tumor diagnosis and as a therapy
these genes may present novel and distinct prediction targets. target.
In addition, the cytidine deaminase gene family To sum up (Table 2), ARMH1, APOBEC3D, APOBEC3F,
(APOBEC3D and APOBEC3F) genes identified in the and PXDNL are either rarely reported or not previously
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 12 doi: 10.36922/td.3469