Page 68 - TD-3-3
P. 68
Tumor Discovery Pyroptosis-related genes in breast cancer progression
A C
B
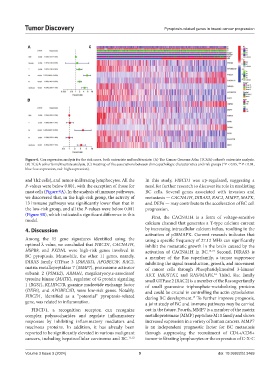
Figure 6. Cox regression analysis for the risk score, both univariate and multivariate. (A) The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort’s univariate analysis.
(B) TCGA cohort’s multivariate analysis. (C) Heatmap of the associations between clinicopathologic characteristics and risk groups (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,
blue: low expression, red: high expression).
and Th2 cells), and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. All the In this study, FIBCD1 was up-regulated, suggesting a
P-values were below 0.001, with the exception of those for need for further research to discover its role in mediating
mast cells (Figure 9A). In the analysis of immune pathways, BC cells. Several genes associated with invasion and
we discovered that, in the high-risk group, the activity of metastasis — CACNA1H, DIRAS3, RAC2, MMP7, MATK,
13 immune pathways was significantly lower than that in and DEF6 — may contribute to the acceleration of BC cell
the low-risk group, and all the P-values were below 0.001 progression.
(Figure 9B), which indicated a significant difference in this First, the CACNA1H is a form of voltage-sensitive
model.
calcium channel that generates a T-type calcium current
4. Discussion by increasing intracellular calcium influx, resulting in the
activation of p38MAPK. Current research indicates that
Among the 15 gene signatures identified using the using a specific frequency of 27.12 MHz can significantly
optimal λ value, we concluded that FIBCD1, CACNA1H, inhibit the metastatic growth in the brain caused by the
HSPB8, and PXDNL were high-risk genes involved in activation of CACNA1H in BC. 13-15 Second, DIRAS3 is
BC pyroptosis. Meanwhile, the other 11 genes, namely, a member of the Ras superfamily, a tumor suppressor
DIRAS family GTPase 3 (DIRAS3), APOBEC3F, RAC2, inhibiting the signal transduction, growth, and movement
matrix metallopeptidase 7 (MMP7), proteasome activator of cancer cells through Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/
subunit 2 (PSME2), ARMH1, megakaryocyte-associated AKT, JAK/STAT, and RAS/MAPK. Third, Rac family
16
tyrosine kinase (MATK), regulator of G protein signaling small GTPase 2 (RAC2) is a member of the Ras superfamily
1 (RGS1), KLHDC7B, guanine nucleotide exchange factor of small guanosine triphosphate-metabolizing proteins
(DEF6), and APOBEC3D, were low-risk genes. Notably, and could be crucial in controlling the actin cytoskeleton
FIBCD1, identified as a “potential” pyroptosis-related during BC development. To further improve prognosis,
17
gene, was related to inflammation. a joint study of BC and immune pathways may be carried
FIBCD1, a recognition receptor, can recognize out in the future. Fourth, MMP7 is a member of the matrix
complex polysaccharides and regulate inflammatory metalloproteinase (MMP) peptidase M10 family and shows
responses by inhibiting inflammatory mediators and increased expression in a variety of human cancers. MMP7
mucinous proteins. In addition, it has already been is an independent prognostic factor for BC metastasis
reported to be significantly elevated in various malignant through suppressing the recruitment of CD4+/CD8+
cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma and BC. 11,12 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or the expression of C-X-C
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/td.3469