Page 136 - TD-3-4
P. 136
Tumor Discovery CTC characterization for EGFR mutations
Table 5. (Continued)
Patient ID Exon EGFR EGFR mutation in CTCs Percentage of mutations Exon EGFR EGFR mutation Matched
CTC detected using NGS biopsy tumor biopsy (Yes or No)
39 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 5.83 WT No
20 T790M 0.83
18 N700D 0.69
40 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 19.67 21 L858R No
20 L841P 1.4
43 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 2.43 WT No
21 V843L 0.53
53 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 8.47 WT No
54 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 1.11 WT No
55 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 14.34 WT No
56 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 3.26 WT No
20 R766H 0.92
57 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 32.64 WT No
58 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 22.85 WT No
59 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 1.66 21 L858R No
Abbreviations: WT: Wild-type (no mutation detected); CTCs: Circulating tumor cells; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; NGS: Next-generation
sequencing. The bold values represent mutations/deletions on exons 18-21 of the EGFR gene.
and has also been associated with partial response to
erlotinib. 57,62-64 A K708R mutation has been reported
in ovarian cancers where it has been associated with
abnormal phosphorylation of AKT and ERK. It has
62
also been reported once in a Chinese study but never in
65
Caucasian populations; thus, the response of this mutation
to TKIs is not clear. These patient-specific point mutations
will potentially offer new insights into treatment responses
and should be analyzed in a large cohort.
The marked disparity in the number of mutations
detected in CTCs (78.95%) when compared to matched
tumor biopsies (13.3%) reported in the current study
differs from that published in other studies. Most of these
studies report a similarity in the number of mutations
in matched CTC and tumor biopsy samples, 38,39,46
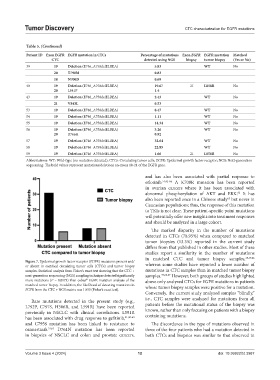
Figure 7. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations present and/
or absent in matched circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and tumor biopsy whereas some studies have reported a lower number of
samples. Statistical analysis from Fisher’s exact test showing that the CTC + mutations in CTC samples than in matched tumor biopsy
next-generation sequencing (NGS) sampling technique detected significantly samples. 37,66,67 However, both groups of studies highlighted
more mutations (P = 0.0173) than cobas EGFR mutation analysis of the above only analyzed CTCs for EGFR mutations in patients
matched tumor biopsy. In addition, the likelihood of detecting mutations in whose tumor biopsy samples were positive for a mutation.
EGFR from the CTC + NGS matrix was 1.855 (Fisher’s exact test).
Conversely, the current study analyzed samples “blindly,”
Rare mutations detected in the present study (e.g., i.e., CTC samples were analyzed for mutations from all
L792P, C797S, H506R, and L591R) have been reported patients before the mutational status of the biopsy was
previously in NSCLC with clinical correlations. L591R known, rather than only focusing on patients with a biopsy
has been associated with drug response to gefitinib, 31,60-63 containing mutations.
and C795S mutation has been linked to resistance to The discordance in the type of mutations observed in
osimertinib. 31,62 D761N mutation has been reported three of the four patients who had a mutation detected in
in biopsies of NSCLC and colon and prostate cancers, both CTCs and biopsies was similar to that observed in
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 12 doi: 10.36922/td.3987