Page 133 - TD-3-4
P. 133
Tumor Discovery CTC characterization for EGFR mutations
Table 2. (Continued)
Patient ID Exon Mutations Percentage of mutations No. of CTCs
detected using NGS counted
18 N700D 0.69
40 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 19.67 5
L841P 1.4
43 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 2.43 41
21 V843L 0.53
53 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 8.47
54 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 1.11
55 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 14.34
56 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 3.26 300
20 R776H 1.34
57 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 32.64 115
58 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 22.85 505
59 19 Deletion (E746_A750delELREA) 1.66 52
Abbreviations: WT: Wild-type (negative for an EGFR mutation); ND: Not done; NR: No result; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor;
CTCs: Circulating tumor cells; NGS: Next-generation sequencing. The bold values represent mutations/deletions on exons 18-21 of the EGFR gene.
A B
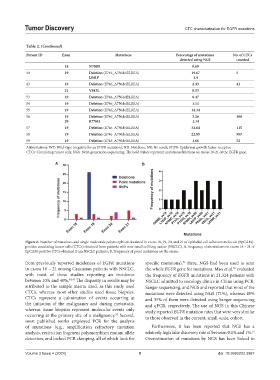
Figure 6. Number of mutations and single nucleotide polymorphism obtained in exons 18, 19, 20, and 21 of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)-
positive circulating tumor cells (CTCs) obtained from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). A, frequency of aberrations on exons 18 – 21 of
EpCAM-positive CTCs obtained from NSCLC patients; B, Frequency of point mutations on the exons.
from previously reported incidences of EGFR mutations specific mutations). Here, NGS had been used to scan
51
in exons 18 – 21 among Caucasian patients with NSCLC, the whole EGFR gene for mutations. Mao et al. evaluated
52
with most of these studies reporting an incidence the frequency of EGFR mutations in 21,324 patients with
between 10% and 40%. 48,49 The disparity in results may be NSCLC admitted to oncology clinics in China using PCR,
attributed to the sample matrix used, as this study used Sanger sequencing, and NGS and reported that most of the
CTCs, whereas most other studies used tissue biopsies. mutations were detected using NGS (71%), whereas 45%
CTCs represent a culmination of events occurring at and 35% of them were detected using Sanger sequencing
the initiation of the malignancy and during metastasis, and qPCR, respectively. The use of NGS in this Chinese
whereas tissue biopsies represent molecular events only study reported EGFR mutation rates that were very similar
occurring at the primary site of a malignancy. Second, to those observed in the current, small-scale, cohort.
50
most published works employed PCR for the analysis
of mutations (e.g., amplification refractory mutation Furthermore, it has been reported that NGS has a
analysis, restriction fragment polymorphism mutant allele relatively high false discovery rate of between 0.1% and 1%.
53
detection, and locked PCR clamping, all of which look for Overestimation of mutations by NGS has been linked to
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/td.3987