Page 128 - TD-3-4
P. 128
Tumor Discovery CTC characterization for EGFR mutations
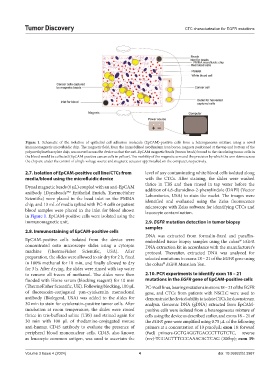
Figure 1. Schematic of the isolation of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)-positive cells from a heterogeneous mixture using a novel
immunomagnetic microfluidic chip. The magnetic field, from the immobilized neodymium iron boron magnets positioned at the top and bottom of the
polymethylmethacrylate chip, was moved across the device so that the anti-EpCAM magnetic beads (brown beads) bound to the circulating tumor cells in
the blood would be collected (EpCAM-positive cancer cells in yellow). The mobility of the magnetic arm and the precision by which the arm skims across
the chip are under the control of a high-voltage source and magnetic actuator app installed on the computer, respectively.
2.7. Isolation of EpCAM-positive cell line/CTCs from level of any contaminating white blood cells isolated along
media/blood using the microfluidic device with the CTCs. After staining, the slides were washed
thrice in TBS and then rinsed in tap water before the
Dynal magnetic beads (6 µL) coupled with an anti-EpCAM
antibody (Dynabeads Epithelial Enrich, ThermoFisher addition of 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (Vector
Laboratories, USA) to stain the nuclei. The images were
Scientific) were placed in the bead inlet on the PMMA identified and evaluated using the Zeiss fluorescence
chip, and 13 mL of media spiked with PC-9 cells or patient microscope with Zeiss software for identifying CTCs and
blood samples were placed in the inlet for blood shown leucocyte contamination.
in Figure 1. EpCAM-positive cells were isolated using the
immunomagnetic unit. 2.9. EGFR mutation detection in tumor biopsy
samples
2.8. Immunostaining of EpCAM-positive cells
DNA was extracted from formalin-fixed and paraffin-
EpCAM-positive cells isolated from the device were embedded tissue biopsy samples using the cobas EGFR
concentrated onto microscope slides using a cytospin DNA extraction kit in accordance with the manufacturer’s
machine (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA). After protocol. Thereafter, extracted DNA was analyzed for
preparation, the slides were allowed to air dry for 2 h, fixed selected mutations in exons 18 – 21 of the EGFR gene using
in 100% methanol for 10 min, and finally allowed to dry the cobas EGFR Mutation Test.
for 3 h. After drying, the slides were rinsed with tap water
to remove all traces of methanol. The slides were then 2.10. PCR experiments to identify exon 18 – 21
flooded with Horse serum (blocking reagent) for 10 min mutations in the EGFR gene of EpCAM-positive cells
(ThermoFisher Scientific, UK). Following blocking, 100 µL PC-9 cell lines, bearing mutations in exons 18 – 21 of the EGFR
of fluorescein-conjugated pan-cytokeratin monoclonal gene, and CTCs from patients with NSCLC were used to
antibody (Biolegend, USA) was added to the slides for demonstrate the device’s ability to isolate CTCs for downstream
30 min to stain for cytokeratin-positive tumor cells. After analysis. Genomic DNA (gDNA) extracted from EpCAM-
incubation at room temperature, the slides were rinsed positive cells were isolated from a heterogeneous mixture of
thrice in tris-buffered saline (TBS) and stained again for cells using the device as described earlier, and exons 18 – 21 of
30 min with 100 µL of rhodamine-conjugated mouse the EGFR gene were amplified using 0.75 µL of the following
anti-human CD45 antibody to evaluate the presence of primers at a concentration of 10 pmol/µL: exon 18: forward
peripheral blood mononuclear cells. CD45, also known (fwd) primers-GCTGAGGTGACCCTTGTCTC, reverse
as leucocyte common antigen, was used to ascertain the (rev)-TGGAGTTTCCCAAACACTCAG (300bp); exon 19:
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/td.3987