Page 116 - TD-4-1
P. 116
Tumor Discovery HHT inhibits pancreatic cancer progress
A
B
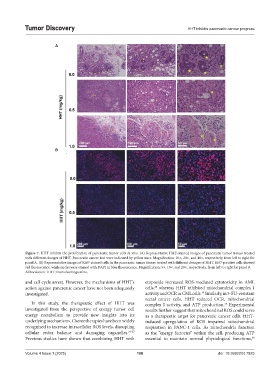
Figure 7. HHT inhibits the proliferation of pancreatic tumor cells in vivo. (A) Representative H&E-stained images of pancreatic tumor tissues treated
with different dosages of HHT. Pancreatic cancer foci were indicated by yellow stars. Magnification: 10×, 20×, and 40×, respectively, from left to right for
panel A. (B) Representative images of Ki67-stained cells in the pancreatic tumor tissues treated with different dosages of HHT. Ki67-positive cells showed
red fluorescence, while nuclei were stained with DAPI in blue fluorescence. Magnification: 5×, 10×, and 20×, respectively, from left to right for panel B.
Abbreviation: HHT: Homoharringtonine.
and cell cycle arrest. However, the mechanisms of HHT’s etoposide increased ROS-mediated cytotoxicity in AML
action against pancreatic cancer have not been adequately cells, whereas HHT inhibited mitochondrial complex I
28
16
investigated. activity and OCR in CML cells. Similarly, in 5-FU-resistant
rectal cancer cells, HHT reduced OCR, mitochondrial
In this study, the therapeutic effect of HHT was complex I activity, and ATP production. Experimental
29
investigated from the perspective of energy tumor cell results further suggest that mitochondrial ROS could serve
energy metabolism to provide new insights into its as a therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer cells. HHT-
underlying mechanisms. Chemotherapies have been widely induced upregulation of ROS impaired mitochondrial
recognized to increase intracellular ROS levels, disrupting respiration in PANC-1 cells. As mitochondria function
cellular redox balance and damaging organelles. 24-27 as the “energy factories” within the cell, producing ATP
Previous studies have shown that combining HHT with essential to maintain normal physiological functions,
30
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 108 doi: 10.36922/td.7825