Page 113 - TD-4-1
P. 113
Tumor Discovery HHT inhibits pancreatic cancer progress
A C
B
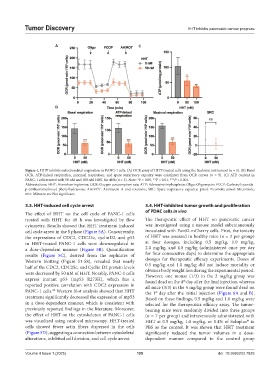
Figure 4. HHT inhibits mitochondrial respiration in PANC-1 cells. (A) OCR assay of HHT-treated cells using the Seahorse instrument (n = 5). (B) Basal
OCR, ATP-linked respiration, maximal respiration, and spare respiratory capacity were calculated from OCR curves (n = 5). (C) ATP content in
PANC-1 cells treated with 50 nM and 100 nM HHT for 48 h (n = 3). Note: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Abbreviations: HHT: Homoharringtonine; OCR: Oxygen consumption rate; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; Oligo: Oligomycin; FCCP: Carbonyl cyanide-
p-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone; AA/ROT: Antimycin A and rotenone; SRC: Spare respiratory capacity; pmol: Picomole; μmol: Micromole;
min: Minutes; ns: Not significant.
3.3. HHT-induced cell cycle arrest 3.4. HHT-inhibited tumor growth and proliferation
of PDAC cells in vivo
The effect of HHT on the cell cycle of PANC-1 cells
treated with HHT for 48 h was investigated by flow The therapeutic effect of HHT on pancreatic cancer
cytometry. Results showed that HHT treatment induced was investigated using a mouse model subcutaneously
cell cycle arrest in the S phase (Figure 5A). Concurrently, inoculated with Pan02-mCherry cells. First, the toxicity
the expressions of CDC2, CDC25c, cyclinD2, and p53 of HHT was assessed in healthy mice (n = 3 per group)
in HHT-treated PANC-1 cells were downregulated in at four dosages, including 0.5 mg/kg, 1.0 mg/kg,
a dose-dependent manner (Figure 5B). Quantification 2.0 mg/kg, and 4.0 mg/kg (administered once per day
results (Figure 5C), derived from the replicates of for four consecutive days) to determine the appropriate
Western blotting (Figure S1-S8), revealed that nearly dosages for therapeutic efficacy experiments. Doses of
half of the CDC2, CDC25c, and Cyclin D2 protein levels 0.5 mg/kg and 1.0 mg/kg did not induce mortality or
were decreased by 50 nM of HHT. Notably, PANC-1 cells obvious body weight loss during the experimental period.
However, one mouse (1/3) in the 2 mg/kg group was
express mutant p53 (mp53 R273H), which has a found dead on the 4 day after the final injection, whereas
th
reported positive correlation with CDC2 expression in all mice (3/3) in the 4 mg/kg group were found dead on
PANC-1 cells. Western blot analysis showed that HHT the 1 day after the initial injection (Figure 6A and B).
22
st
treatment significantly decreased the expression of mp53 Based on these findings, 0.5 mg/kg and 1.0 mg/kg were
in a dose-dependent manner, which is consistent with selected for the therapeutics efficacy assay. The tumor-
previously reported findings in the literature. Moreover, bearing mice were randomly divided into three groups
the effect of HHT on the cytoskeleton of PANC-1 cells (n = 7 per group) and intravenously administrated with
was visualized using confocal microscopy. HHT-treated HHT at 0.5 mg/kg, 1.0 mg/kg, or 0.4% of Soluplus in
®
cells showed fewer actin fibers dispersed in the cells PBS as the control. It was shown that HHT treatment
(Figure 5D), suggesting a connection between cytoskeletal significantly reduced the tumor volumes in a dose-
alterations, inhibited cell division, and cell cycle arrest. dependent manner compared to the control group
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 105 doi: 10.36922/td.7825