Page 97 - TD-4-1
P. 97
Tumor Discovery Identification of a potential KRAS(G12C) inhibitor
A B
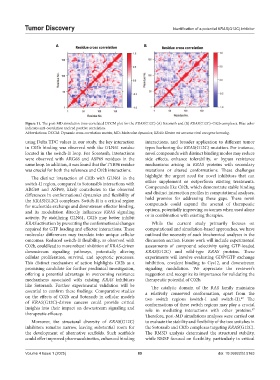
Figure 11. The post-MD simulation time-correlated DCCM plot for the KRAS(G12C) (A) Sotorasib and (B) KRAS(G12C)–C02b complexes. Blue color
indicates anti-correlation and red positive correlation.
Abbreviations: DCCM: Dynamic cross-correlation matrix; MD: Molecular dynamics; KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog.
using Delta TDC values in our study, the key interaction interactions, and broader application to different tumor
in C02b binding was observed with the GLN61 residue types harboring the KRAS(G12C) mutation. For instance,
located in the switch-II loop. For Sotorasib, interactions novel compounds with distinct binding modes may reduce
were observed with ARG68 and ASP69 residues in the side effects, enhance tolerability, or bypass resistance
same loop. In addition, it was found that the TYR96 residue mechanisms arising in KRAS proteins with secondary
was crucial for both the reference and C02b interactions. mutations or altered conformations. These challenges
The distinct interaction of C02b with GLN61 in the highlight the urgent need for novel inhibitors that can
switch-II region, compared to Sotorasib’s interactions with either supplement or outperform existing treatments.
ARG68 and ASP69, likely contributes to the observed Compounds like C02b, which demonstrate stable binding
differences in conformational dynamics and flexibility of and distinct interaction profiles in computational analyses,
the KRAS(G12C) complexes. Switch-II is a critical region hold promise for addressing these gaps. These novel
for nucleotide exchange and downstream effector binding, compounds could expand the arsenal of therapeutic
and its modulation directly influences KRAS signaling options, potentially improving outcomes when used alone
activity. By stabilizing GLN61, C02b may better inhibit or in combination with existing therapies.
KRAS activation by preventing the conformational changes While the current study primarily focuses on
required for GTP loading and effector interactions. These computational and simulation-based approaches, we have
molecular differences may translate into unique cellular outlined the necessity of such biochemical analyses in the
outcomes. Reduced switch-II flexibility, as observed with discussion section. Future work will include experimental
C02b, could lead to more robust inhibition of KRAS-driven assessments of compound selectivity using GTP-loaded
downstream signaling pathways, potentially altering KRAS(G12C) and wild-type KRAS proteins. These
cellular proliferation, survival, and apoptotic processes. experiments will involve evaluating GDP/GTP exchange
This distinct mechanism of action highlights C02b as a inhibition, covalent binding to Cys12, and downstream
promising candidate for further preclinical investigation, signaling modulation. We appreciate the reviewer’s
offering a potential advantage in overcoming resistance suggestion and recognize its importance for validating the
mechanisms associated with existing KRAS inhibitors therapeutic potential of C02b.
like Sotorasib. Further experimental validation will be The catalytic domain of the RAS family maintains
essential to confirm these findings. Comparative studies a relatively conserved conformation, apart from the
on the effects of C02b and Sotorasib in cellular models two switch regions (switch-I and switch-II). The
47
of KRAS(G12C)-driven cancers could provide critical conformations of these switch regions may play a crucial
insights into their impact on downstream signaling and role in mediating interactions with other proteins.
47
therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, post-MD simulations analyses were carried out
Moreover, the structural diversity of KRAS(G12C) to evaluate the stability and flexibility of the two switches in
inhibitors remains narrow, leaving substantial room for the Sotorasib and C02b complexes targeting KRAS(G12C).
the development of alternative scaffolds. Such scaffolds The RMSD analysis determined the structural stability,
could offer improved pharmacokinetics, enhanced binding while RMSF focused on flexibility, particularly in critical
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 89 doi: 10.36922/td.5163