Page 94 - TD-4-2
P. 94
Tumor Discovery SNPs rs9929218 and rs6983267 in Kurdish CRC
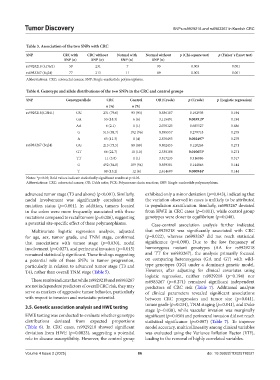
Table 3. Association of the two SNPs with CRC
SNP CRC with CRC without Normal with Normal without p (Chi‑square test) p (Fisher`s Exact test)
SNP (n) SNP (n) SNP (n) SNP (n)
rs9929218 (CDH1) 59 231 7 93 0.003 0.001
rs6983267 (8q24) 77 213 11 89 0.002 0.001
Abbreviations: CRC: colorectal cancer; SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Table 4. Genotype and allele distributions of the two SNPs in the CRC and control groups
SNP Genotype/allele CRC Control OR (Crude) p (Crude) p (Logistic regression)
n (%) n (%)
rs9929218(CDH1) GG 231 (79.6) 93 (93) 0.836187 0.192903 0.194
GA 53 (18.3) 6 (6) 3.115491 0.003919* 0.194
AA 6 (2.1) 1 (1) 2.076125 0.685527 0.686
G 515 (88.7) 192 (96) 0.895557 0.279718 0.279
A 65 (11.3) 8 (4) 2.876493 0.002497* 0.279
rs6983267 (8q24) GG 213 (73.5) 89 (89) 0.802455 0.120263 0.271
GT 66 (22.7) 10 (10) 2.330108 0.010653* 0.271
TT 11 (3.8) 1 (1) 3.817235 0.316886 0.317
G 492 (84.8) 189 (94) 0.859381 0.144846 0.144
T 88 (15.2) 12 (6) 2.614609 0.000944* 0.144
Notes: *p<0.05; Bold values indicate statistically significant results at p<0.05.
Abbreviations: CRC: colorectal cancer; OR: Odds ratio; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphism.
advanced tumor stage (T3 and above) (p<0.001). Similarly, exhibited only a minor deviation (p=0.043), indicating that
nodal involvement was significantly correlated with the variation observed in cases is unlikely to be attributed
mutation status (p=0.001). In addition, tumors located to population stratification. Similarly, rs6983267 deviated
in the colon were more frequently associated with these from HWE in CRC cases (p=0.011), while control group
mutations compared to rectal tumors (p=0.006), suggesting genotypes were closer to equilibrium (p=0.048).
a potential site-specific effect of these polymorphisms. Case-control association analysis further indicated
Multivariate logistic regression analysis, adjusted that rs9929218 was significantly associated with CRC
for age, sex, tumor grade, and TNM stage, confirmed (p=0.022), whereas rs6983267 did not reach statistical
that associations with tumor stage (p=0.030), nodal significance (p=0.090). Due to the low frequency of
involvement (p=0.027), and perineural invasion (p=0.015) homozygous mutant genotypes (AA for rs9929218
remained statistically significant. These findings suggesting and TT for rs6983267), the analysis primarily focused
a potential role of these SNPs in tumor progression, on comparing heterozygotes (GA and GT) with wild-
particularly in relation to advanced tumor stage (T3 and type genotypes (GG) under a dominant genetic model.
T4), rather than overall TNM stage (Table 5). However, after adjusting for clinical covariates using
logistic regression, neither rs9929218 (p=0.194) nor
These results indicate that while rs9929218 and rs6983267 rs6983267 (p=0.271) remained significant independent
are not independent predictors of overall CRC risk, they may predictors of CRC risk (Table 7). Additional analysis
serve as markers of aggressive tumor behavior, particularly of clinical parameters revealed significant associations
with respect to invasion and metastatic potential. between CRC progression and tumor size (p=0.041),
tumor grade (p=0.034), TNM staging (p=0.041), and Duke
3.5. Genetic association analysis and HWE testing
stage (p=0.038), while vascular invasion was marginally
HWE testing was conducted to evaluate whether genotype significant (p=0.050) and perineural invasion did not reach
distributions deviated from expected proportions statistical significance (p=0.087) (Table 7). To improve
(Table 6). In CRC cases, rs9929218 showed significant model accuracy, multicollinearity among clinical variables
deviation from HWE (p=0.0023), suggesting a potential was evaluated using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF),
role in disease susceptibility. However, the control group leading to the removal of highly correlated variables.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 86 doi: 10.36922/TD025110021