Page 44 - TD-4-3
P. 44
Tumor Discovery HRD genomic alterations in Chinese NSCLC
A
B
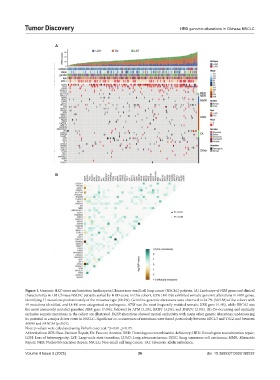
Figure 1. Genomic HRD score and mutation landscape in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. (A) Landscape of HRR genes and clinical
characteristics in 158 Chinese NSCLC patients sorted by HRD score. In this cohort, 8.9% (14/158) exhibited somatic genomic alterations in HRR genes,
identifying 17 mutations predominantly of the missense type (88.2%). Germline genomic alterations were observed in 24.7% (39/158) of the cohort with
49 mutations identified, and 18.4% were categorized as pathogenic. ATM was the most frequently mutated somatic HRR gene (4.4%), while BRCA2 was
the most commonly mutated germline HRR gene (7.0%), followed by ATM (3.2%), BRIP1 (3.2%), and BARD1 (2.5%). (B) Co-occurring and mutually
exclusive somatic mutations in the cohort are illustrated. EGFR alterations showed mutual exclusivity with many other genetic alterations, underscoring
its potential as a major driver event in NSCLC. Significant co-occurrences of mutations were found particularly between ERCC3 and TSC2, and between
MSH6 and FANCM (p<0.01).
Note: p-values were calculated using Fisher’s exact test: *p<0.01, p<0.05.
Abbreviations: BER: Base-Excision Repair; FA: Fanconi Anemia; HRD: Homologous recombination deficiency; HRR: Homologous recombination repair;
LOH: Loss of heterozygosity; LST: Large-scale state transition; LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC: Lung squamous cell carcinoma; MMR: Mismatch
Repair; NER: Nucleotide Excision Repair; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; TAI: Telomeric allelic imbalance.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 36 doi: 10.36922/TD025180032