Page 49 - TD-4-3
P. 49
Tumor Discovery HRD genomic alterations in Chinese NSCLC
A B
C D
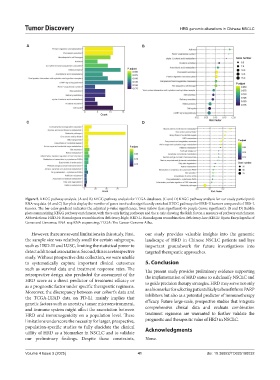
Figure 5. KEGG pathway analysis. (A and B) KEGG pathway analysis for TCGA databases. (C and D) KEGG pathway analysis for our study participant’s
RNA-seq data. (A and C) Bar plots display the number of genes involved in significantly enriched KEGG pathways for HRD-H tumors compared to HRD-L
tumors. The bar color gradient indicates the adjusted p-value significance, from yellow (less significant) to purple (more significant). (B and D) Bubble
plots summarizing KEGG pathway enrichment, with the y-axis listing pathways and the x-axis showing the Rich factor, a measure of pathway enrichment.
Abbreviations: HRD-H: Homologous recombination deficiency-high; HRD-L: Homologous recombination deficiency-low; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of
Genes and Genomes; RNA-seq: RNA sequencing; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
However, there are several limitations in this study. First, our study provides valuable insights into the genomic
the sample size was relatively small for certain subgroups, landscape of HRD in Chinese NSCLC patients and lays
such as HRD-H and LUSC, limiting the statistical power to important groundwork for future investigations into
detect additional associations. Second, this is a retrospective targeted therapeutic approaches.
study. Without prospective data collection, we were unable
to systematically capture important clinical outcomes 5. Conclusion
such as survival data and treatment response rates. The The present study provides preliminary evidence supporting
retrospective design also precluded the assessment of the the implementation of HRD status to subclassify NSCLC and
HRD score as a direct predictor of treatment efficacy or to guide precision therapy strategies. HRD may serve not only
as a prognostic factor under specific therapeutic regimens. as a biomarker for selecting patients likely to benefit from PARP
Moreover, the discrepancy between our cohort’s data and
the TCGA-LUAD data on PD-L1 mainly implies that inhibitors but also as a potential predictor of immunotherapy
genetic factors such as ancestry, tumor microenvironment, efficacy. Future large-scale, prospective studies that integrate
and immune system might affect the association between comprehensive clinical data and evaluate combination
HRD and immunogenicity on a population level. These treatment regimens are warranted to further validate the
limitations underscore the necessity for larger, prospective, prognostic and therapeutic value of HRD in NSCLC.
population-specific studies to fully elucidate the clinical Acknowledgments
utility of HRD as a biomarker in NSCLC and to validate
our preliminary findings. Despite these constraints, None.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 41 doi: 10.36922/TD025180032