Page 48 - TD-4-3
P. 48
Tumor Discovery HRD genomic alterations in Chinese NSCLC
A B
C D
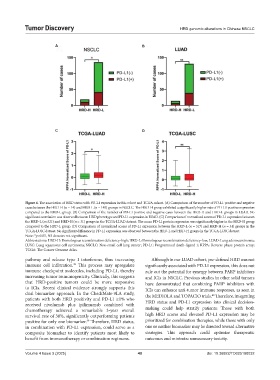
Figure 4. The association of HRD status with PD-L1 expression in this cohort and TCGA cohort. (A) Comparison of the number of PD-L1 positive and negative
cases between the HRD-H (n = 14) and HRD-L (n = 140) groups in NSCLC. The HRD-H group exhibited a significantly higher rate of PD-L1 positive expression
compared to the HRD-L group. (B) Comparison of the number of PD-L1 positive and negative cases between the HRD-H and HRD-L groups in LUAD. No
significant correlation was observed between HRD phenotype and PD-L1 expression in LUAD. (C) Comparison of normalized scores of PD-L1 expression between
the HRD-L (n=321) and HRD-H (n = 31) groups in the TCGA-LUAD dataset. The mean PD-L1 protein expression was significantly higher in the HRD-H group
compared to the HRD-L group. (D) Comparison of normalized scores of PD-L1 expression between the HRD-L (n = 317) and HRD-H (n = 31) groups in the
TCGA-LUSC dataset. No significant difference in PD-L1 expression was observed between the HRD-L and HRD-H groups in the TCGA-LUSC dataset.
Note: *p<0.05, NS denotes not significant.
Abbreviations: HRD-H: Homologous recombination deficiency-high; HRD-L: Homologous recombination deficiency-low; LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma;
LUSC: Lung squamous cell carcinoma; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; RPPA: Reverse phase protein array;
TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
pathway and release type I interferons, thus increasing Although in our LUAD cohort, pre-defined HRD was not
immune cell infiltration. This process may upregulate significantly associated with PD-L1 expression, this does not
38
immune checkpoint molecules, including PD-L1, thereby rule out the potential for synergy between PARP inhibitors
increasing tumor immunogenicity. Clinically, this suggests and ICIs in NSCLC. Previous studies in other solid tumors
that HRD-positive tumors could be more responsive have demonstrated that combining PARP inhibitors with
to ICIs. Recent clinical evidence strongly supports this ICIs can enhance anti-tumor immune responses, as seen in
dual biomarker approach. In the CheckMate-9LA study, the MEDIOLA and TOPACIO trials. Therefore, integrating
40
patients with both HRD positivity and PD-L1 ≥1% who HRD status and PD-L1 expression into clinical decision-
received nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with
chemotherapy achieved a remarkable 3-year overall making could help stratify patients: Those with both
survival rate of 38%, significantly outperforming patients high HRD scores and elevated PD-L1 expression may be
positive for only one biomarker. Therefore, HRD status, prioritized for combination therapies, while those with only
39
in combination with PD-L1 expression, could serve as a one or neither biomarker may be directed toward alternative
composite biomarker to identify patients most likely to strategies. This approach could optimize therapeutic
benefit from immunotherapy or combination regimens. outcomes and minimize unnecessary toxicity.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 40 doi: 10.36922/TD025180032