Page 46 - TD-4-3
P. 46
Tumor Discovery HRD genomic alterations in Chinese NSCLC
A B
C D
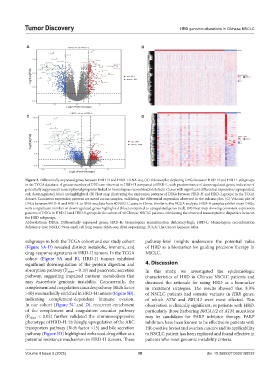
Figure 2. Differentially expressed genes between HRD-H and HRD-L RNA-seq. (A) Volcano plot depicting DEGs between HRD-H and HRD-L subgroups
in the TCGA database. A greater number of DEGs are observed in HRD-H compared to HRD-L, with predominance of downregulated genes, indicative of
potentially suppressed transcriptional programs linked to homologous recombination defects. Genes with significant differential expression (upregulated,
red; downregulated, blue) are highlighted. (B) Heat map illustrating the expression patterns of DEGs between HRD-H and HRD-L groups in the TCGA
dataset. Consistent expression patterns are noted across samples, validating the differential expression observed in the volcano plot. (C) Volcano plot of
DEGs between HRD-H and HRD-L in RNA-seq data from 40 NSCLC cases in China. Similar to the TCGA analysis, HRD-H samples exhibit more DEGs,
with a significant number of downregulated genes highlighted (blue) compared to upregulated genes (red). (D) Heat map showing consistent expression
patterns of DEGs in HRD-H and HRD-L groups in the cohort of 40 Chinese NSCLC patients, reinforcing the observed transcriptomic disparities between
the HRD subgroups.
Abbreviations: DEGs: Differentially expressed genes; HRD-H: Homologous recombination deficiency-high; HRD-L: Homologous recombination
deficiency-low; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; RNA-seq: RNA sequencing; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas.
subgroups in both the TCGA cohort and our study cohort pathway-level insights underscore the potential value
(Figure 5A-D) revealed distinct metabolic, immune, and of HRD as a biomarker for guiding precision therapy in
drug-response signatures in HRD-H tumors. In the TCGA NSCLC.
cohort (Figure 5A and B), HRD-H tumors exhibited
significant downregulation of the protein digestion and 4. Discussion
absorption pathway (P adjust ≈ 0.10) and pancreatic secretion In this study, we investigated the epidemiologic
pathway, suggesting impaired nutrient metabolism that characteristics of HRD in Chinese NSCLC patients and
may exacerbate genomic instability. Concurrently, the discussed the rationale for using HRD as a biomarker
complement and coagulation cascades pathway (Rich factor in treatment strategies. The results showed that 8.9%
>10) was markedly enriched in HRD-H tumors (Figure 5B), of NSCLC patients had somatic variants in HRR genes,
indicating complement-dependent immune evasion. of which ATM and BRCA2 were most affected. This
In our cohort (Figure 5C and D), recurrent enrichment observation is clinically significant, as patients with HRD,
of the complement and coagulation cascades pathway particularly those harboring BRCA1/2 or ATM mutations
(P adjust < 0.05) further validated the immunosuppressive may be candidates for PARP inhibitor therapy. PARP
phenotype of HRD-H. Strikingly, upregulation of the ABC inhibitors have been known to be effective in patients with
transporters pathway (Rich factor >15) and bile secretion HR-positive breast and ovarian cancers and its applicability
pathway (Figure 5D) highlighted enhanced drug efflux as a to NSCLC patient has been explored and found effective in
potential resistance mechanism in HRD-H tumors. These patients who meet genomic instability criteria.
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 38 doi: 10.36922/TD025180032