Page 17 - manuscript_ijb05583
P. 17
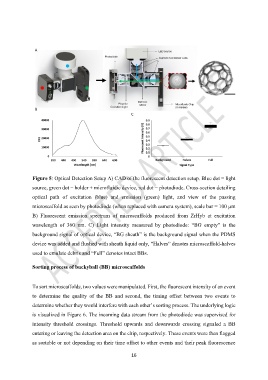
Figure 5: Optical Detection Setup A) CAD of the fluorescent detection setup. Blue dot = light
source, green dot = holder + microfluidic device, red dot = photodiode. Cross-section detailing
optical path of excitation (blue) and emission (green) light, and view of the passing
microscaffold as seen by photodiode (when replaced with camera system), scale bar = 100 µm
B) Fluorescent emission spectrum of microscaffolds produced from ZrHyb at excitation
wavelength of 360 nm. C) Light intensity measured by photodiode: “BG empty” is the
background signal of optical device, “BG sheath” is the background signal when the PDMS
device was added and flushed with sheath liquid only, “Halves” denotes microscaffold-halves
used to emulate debris and “Full” denotes intact BBs.
Sorting process of buckyball (BB) microscaffolds
To sort microscaffolds, two values were manipulated. First, the fluorescent intensity of an event
to determine the quality of the BB and second, the timing offset between two events to
determine whether they would interfere with each other’s sorting process. The underlying logic
is visualized in Figure 6. The incoming data stream from the photodiode was supervised for
intensity threshold crossings. Threshold upwards and downwards crossing signaled a BB
entering or leaving the detection area on the chip, respectively. These events were then flagged
as sortable or not depending on their time offset to other events and their peak fluorescence
16