Page 86 - AIH-1-2
P. 86
Artificial Intelligence in Health Combating XDR-bacteria as we approach 2050
quantum number. For data analysis, NMR absorption by adding an adenyl group to them. In Figure 3, we have
spectra were adjusted to the chemical shift (δ) using presented the classification of different mdr genes and their
tetramethylsilane (TMS) as a standard, and the data were emergence over time. This depiction underscores the rapid
expressed as ppm (parts per million). Tetramethylsilane evolution of mdr genes in response to the introduction of
is chemically inert, magnetically isotropic, miscible a new antibiotic derivative, conferring upon bacteria the
with most organic solvents, and absorbs at a higher capability to neutralize new drugs. Nowadays, bacterial
frequency compared to common types of organic protons. plasmids acquire DNA nikase, DNA topoisomerases, DNA
Equation III is used to calculate the δ: integrases, transposes, and integrons in such a way that,
δ =Δv × 10 /oscillator frequency in cps (III) when exposed to a new chemical, the bacteria begin to
6
rearrange on plasmids to create a new mdr gene. Table 2
Where Δv is the difference in magnetic spin absorption demonstrates the accumulation of mdr genes in both large
frequencies of the sample and the reference in cps (cps is and small bacterial plasmids. It includes an example of
approximately 700 cycles/s). the generation of large plasmids that were sequenced and
obtained from the NCBI GenBank Database (www.ncbi.
2.10. RNA polymerase assay
nlm.nih.gov/nucleotide) by putting the accession number
The RNA polymerase assay was conducted using 0.2 mM (Table 2). We downloaded the plasmid sequences
XTPs, 10 mM MgCl , 1 unit RNA of polymerase, 200 ng and performed multi-alignment to see the percentage
2
denatured CT-DNA, and 10 µci α-P -UTP. The reaction similarities among them because such different plasmids
32
was carried out at 35°C for 15 min, after which it was had many common mdr genes. 17
spotted on diethylaminoethyl (DEAE) paper and washed
with 0.5 M sodium phosphate, followed by ethanol. The It is challenging to develop a new mdr gene against a
dried paper was then counted on a scintillation counter. new antibiotic. However, in the expansive environment
The RNA polymerase assay was performed at the Indian of soil, water, and the intestines of humans and animals,
Institute of Science, specifically in Prof. Dipankar nature’s laboratories surpass human research laboratories.
Chatterjee’s laboratory. A more recent fluorometric RNA This is because environmental bacteria are acquiring
polymerase assay using plasmid DNA as a template was newer mdr genes via conjugation from MDR-bacterial
conducted at Bose Institute (Dr. Jayanta Mukhopadhyay’s plasmids at a rate of approximately a 5% increase
laboratory). 15 per year. At present, the Ganges River water hosts
45 – 50% ampicillin-resistant bacteria, but the percentage
3. Results and discussion of cefotaxime-resistant bacteria is much lower at 5%.
However, imipenem-resistant bacteria are challenging to
3.1. Mechanism of mdr genes’ function and drug detect in Ganga River bacteria using conventional plating
resistance assays with 0.1 mL water on a 10 cm LB+agar+1 mg/mL
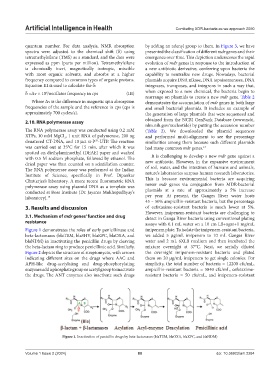
Figure 1 demonstrates the roles of early penicillinase and imipenem plate. To isolate the imipenem-resistant bacteria,
beta-lactamases (blaTEM, blaSHV, blaKPC, blaOXA, and we added 5 µg/mL imipenem to 10 mL Ganges River
blaNDM) in inactivating the penicillin drugs by cleaving water and 2 mL 6XLB medium and then incubated the
the beta-lactam ring to produce penicillinic acid. Similarly, mixture overnight at 37°C. Next, we serially diluted
Figure 2 depicts the structure of streptomycin, with arrows the overnight imipenem-resistant bacteria and plated
indicating different sites on the drugs where AAC and them on 20 µg/mL imipenem to get single colonies. For
APH-like drug-acetylating and drug-phosphorylating simplicity, the total number of bacteria = 12200 cfu/mL,
enzymes add a phosphate group or acetyl group to inactivate ampicillin-resistant bacteria = 5840 cfu/mL, cefotaxime-
the drugs. The ANT enzymes also inactivate such drugs resistant bacteria = 50 cfu/mL, and imipenem-resistant
Figure 1. Inactivation of penicillin drugs by beta-lactamases (blaTEM, blaOXA, blaKPC, and blaNDM)
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 80 doi: 10.36922/aih.2284