Page 91 - AIH-1-2
P. 91
Artificial Intelligence in Health Combating XDR-bacteria as we approach 2050
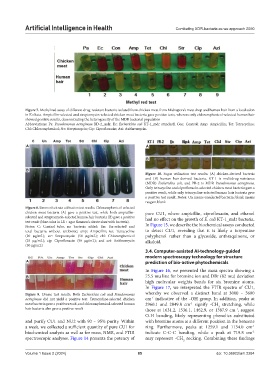
Figure 7. Methyl red assay of different drug-resistant bacteria isolated from chicken meat from Midnapore’s meat shop and human hair from a local salon
in Kolkata. Ampicillin-selected and streptomycin-selected chicken meat bacteria gave positive tests, whereas only chloramphenicol-selected human hair
showed positive results, demonstrating the heterogeneity of the MDR bacterial population
Abbreviations: Pa: Pseudomonas aeruginosa BD-2_mdr; Ec: Escherichia coli KT-1_mdr standard; Con: Control; Amp: Ampicillin; Tet: Tetracycline;
Chl: Chloramphenicol; Str: Streptomycin; Cip: Ciprofloxacin; Azi: Azithromycin.
A A
B
B
Figure 10. Sugar utilization test results. (A) chicken-derived bacteria
and (B) human hair-derived bacteria. KT-1 is multidrug-resistance
(MDR) Escherichia coli, and PB-2 is MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Only tetracycline and ciprofloxacin-selected chicken meat bacteria gave a
positive result, while only tetracycline-selected human hair bacteria gave
a positive test result. Notes: Un means unselected bacteria; blank means
reagent blank
Figure 8. Simmon’s citrate utilization test results. Chloramphenicol-selected
chicken meat bacteria (A) gave a positive test, while both ampicillin- pure CU1, where ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, and ethanol
selected and streptomycin-selected human hair bacteria (B) gave a positive had no effect on the growth of E. coli KT-1_mdr bacteria.
test result (blue color in LB + agar Simmon’s citrate slant with bacteria).
Notes: C: Control tube, no bacteria added; Un: Un-selected and In Figure 15, we describe the biochemical assays conducted
total bacteria without antibiotic; amp: Ampicillin; tet: Tetracycline to detect CU1, revealing that it is likely a turpentine
(20 µg/mL); str: Streptomycin (50 µg/mL); chl: Chloramphenicol polyphenol rather than a glycoside, anthraquinone, or
(25 µg/mL); cip: Ciprofloxacin (50 µg/mL); and azi: Azithromycin alkaloid.
(50 µg/mL)
3.4. Computer-assisted AI-technology-guided
modern spectroscopy technology for structure
A prediction of bio-active phytochemicals
In Figure 16, we presented the mass spectra showing a
B 75.5 mu line for bromine ion and DBr (82 mu) deviation
high molecular weights bands for six bromine atoms.
In Figure 17, we interpreted the FTIR spectra of CU1,
Figure 9. Urease test results. Both Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas whereby we observed a distinct band at 3000 – 3600
-1
aeruginosa did not yield a positive test. Tetracycline-selected chicken cm indicative of the -OH group. In addition, peaks at
meat bacteria gave a positive result, and chloramphenicol-selected human 2960.1 and 2849.8 cm signify -CH stretching, while
-1
3
hair bacteria also gave a positive result those at 1631.2, 1536.1, 1462.9, or 1387.9 cm , suggest
-1
O-H bending, likely representing phenolics substituted
and purify CU1 and NU2 with 90 – 95% purity. Within with bromine atoms at a different position in the benzene
a week, we collected a sufficient quantity of pure CU1 for ring. Furthermore, peaks at 1259.1 and 1134.0 cm
-1
biochemical analysis as well as for mass, NMR, and FTIR indicate C-C-C bending, while a peak at 719.8 cm
-1
spectroscopic analyses. Figure 14 presents the potency of may represent -CH rocking. Combining these findings
2
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 85 doi: 10.36922/aih.2284