Page 93 - AIH-1-2
P. 93
Artificial Intelligence in Health Combating XDR-bacteria as we approach 2050
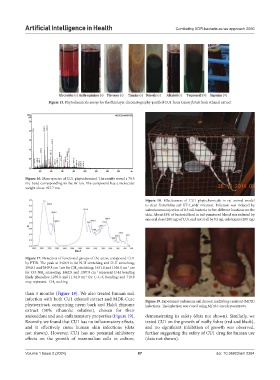
Figure 15. Phytochemicals assays for the thin layer chromatography-purified CU1 from Cassia fistula bark ethanol extract
Figure 16. Mass-spectra of CU1 phytochemical. The results reveal a 79.5
mu band corresponding to the Br ion. The compound has a molecular
-
weight above 927.7 mu
Figure 18. Effectiveness of CU1 phytochemicals in rat animal model
to clear Escherichia coli KT-1_mdr infection. Infection was induced by
subcutaneous injection of 0.5 mL bacteria in five different locations on the
skin. About 83% of bacterial load in tail-punctured blood was reduced by
one oral dose (200 mg) of CU1 and not at all by 0.5 mL cefotaxime (200 mg)
Figure 17. Detection of functional groups of the active compound CU1
by FTIR. The peak at 3426.9 is for N-H stretching and O-H stretching;
2960.1 and 2849.8 cm are for CH stretching; 1631.8 and 1536.1 cm are
-1
-1
3
for CO-NH scissoring; 1462.9 and 1387.9 cm represent O-H bending
-1
2
likely phenolics; 1259.1 and 11.34.0 cm for C-C-C bending; and 719.8
-1
may represent -CH rocking
2
than 3 months (Figure 18). We also treated human nail
infection with both CU1 ethanol extract and MDR-Cure Figure 19. Experiment on human nail chronic multidrug-resistant (MDR)
phytoextract, comprising neem bark and Haldi rhizome infections. The infection was cured using MDR-Cure phytoextracts
extract (50% ethanolic solution), chosen for their
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (Figure 19). demonstrating its safety (data not shown). Similarly, we
Recently, we found that CU1 has no inflammatory effects, tested CU1 on the growth of molly fishes (red and black),
and it effectively cures human skin infections (data and no significant inhibition of growth was observed,
not shown). However, CU1 has no potential inhibitory further suggesting the safety of CU1 drug for human use
effects on the growth of mammalian cells in culture, (data not shown).
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 87 doi: 10.36922/aih.2284