Page 87 - AIH-1-2
P. 87
Artificial Intelligence in Health Combating XDR-bacteria as we approach 2050
bacteria = 0.2 cfu/mL. Therefore, the chance of infection infection, and the doctor prescribed the cefotaxime drug,
by imipenem-resistant bacteria is approximately 579 times which was proven effective. However, to avoid the risk of
lower than that of ampicillin-resistant bacteria by bathing MDR development, the author was subsequently prescribed
or consuming Ganges River water. Thus, more people may two higher derivatives of tetracycline and aminoglycoside
be infected by ampicillin-resistant bacteria and still be antibiotics. Fast forward to 2050, and a similar scenario
cured with cefotaxime and imipenem drugs. may unfold differently. For instance, if the author were to
Certainly, in 2050, when the percentage of imipenem- bathe in the Ganges River, the initial cefotaxime treatment
resistant bacteria has increased, the situation will be may not be effective, and if amikacin was also ineffective,
different. It will be simpler to identify imipenem-resistant then hospitalization would be recommended, usually
bacteria by plating 0.1 mL Ganges river water onto a 10 cm accompanied by drug-sensitivity testing. In such cases,
LB + agar + imipenem plate. In 2050, doctors are likely doripenem and meropenem therapy may be considered
to perform drug sensitivity assays first using 100 antibiotic next, but if the totally drug-resistant (TDR) infection or if
paper disks to determine the nature of a patient’s blood, all 100 available antibiotics in Kolkata medical stores have
whether it is an MDR, extensively drug-resistant (XDR), failed, then the doctor would seek help from the USA to
or IDR infection. Obtaining such an assay result may cost a obtain expensive and high-risk investigational drugs. This is
few thousand rupees, and one may have to wait for 2 days why scientists have predicted that there could be 10 million
in order for the doctor to prescribe the correct antibiotic. deaths in Asia annually by 2050. Simply put, people will not
One of the authors (Asit Kumar Chakraborty) shares a be able to afford the costly therapy, leading to their demise.
personal experience here. In 2022, the author contrasted an In this paper, we have demonstrated the inactivation
mechanism by diverged penicillinases (Figure 1) and
have also demonstrated the acetylation, adenylation, and
phosphorylation of different aminoglycosides acetyl-
transferase (AAC), aminoglycoside adenyl-transferase
(AAD), and aminoglycoside phosphotransferase (APH)
enzymes (Figure 2). In addition, we have depicted the
gradual discovery of new antibiotics with the subsequent
generation of new mdr genes to inactivate these new
antibiotics (Figure 3). This ongoing process has been
occurring since 1970 until the present day, and doctors
are becoming increasingly exhausted by the continuous
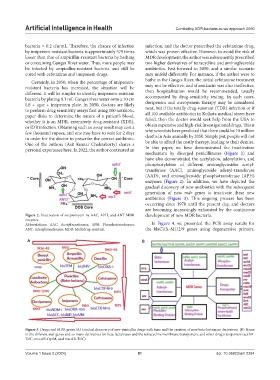
Figure 2. Inactivation of streptomycin by AAC, APH, and ANT MDR development of new MDR bacteria.
enzymes
Abbreviations: AAC: Acetyltransferases; APH: Phosphotransferases; In Figure 4, we presented the PCR assay results for
ANT: Adenyltransferases; MDR: Multidrug-resistant. the blaCTX-M1/2/9 genes using degenerative primers.
A B
Figure 3. Drugs and MDR genes (A) Gradual discovery of new penicillin drugs with time and the creation of new beta-lactamase derivatives. (B) Name
of the different mdr genes and so many derivatives for beta-lactamases and the tetracycline membrane transporters, and other drug transporters (acrAB-
TolC, mexAB-OprM, and macAB-TolC)
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2024) 81 doi: 10.36922/aih.2284