Page 74 - AIH-1-3
P. 74
Artificial Intelligence in Health Rotational thermography for breast cancer screening
the camera at a particular angle to capture the required IR imaging system to generate appropriate images considering
breast images. These steps are detailed in Table 2. After variations in temperature and other physical conditions
allowing the ambient temperature to reduce by 2°C through that influence imaging. Hence, detailed knowledge and
the temperature controller of the air conditioner (AC), the appropriate system adaptation are essential. Without such
second set of data was acquired. Accordingly, 32 IR breast intelligent data collection processes, data analysis is crucial
images were collected over both ambient temperatures. for algorithmic perfection and improved machine learning
This method is termed dynamic temperature-based data performance. Therefore, integrating data collection
9,11
collection. and analysis while exploring the impact of environmental
Protocol-wise, the room temperature is adjusted for each conditions on IR imaging is essential and required at every
subject in the FS. Controlling the room’s temperature and step for optimal system performance.
maintaining it at a specific value effectively and quickly was While some researchers have developed data collection
difficult for each patient. The tabletop rotating mechanical protocols, the data analysis algorithms are unsuitable for
setup placed the IR image-capturing system in an airtight integration with IR image processing techniques, resulting
chamber to overcome this problem. The temperature in poor execution for the breast cancer screening system.
inside this chamber was externally regulated through a This study integrated IR image processing techniques
portable AC. The room temperature was maintained at a into the system at every stage, leading to efficient system
constant value through the room AC. This setup is shown development and gradual software evolution. This results
in Figure 4. in an effective IR image processing algorithm. Previous
studies used online databases like Thermalytix to
37
2.2. Data analysis develop IR imaging algorithms. However, its real-life
In thermal imaging, the camera is the primary device for implementation had a limitation as this database needs
acquiring the data to be analyzed for breast cancer screening. more information for such development. Therefore, a novel
While previous studies are based on this methodology, data collection protocol was developed and implemented
their technique is different and not in consonance with the in the FS to overcome this limitation.
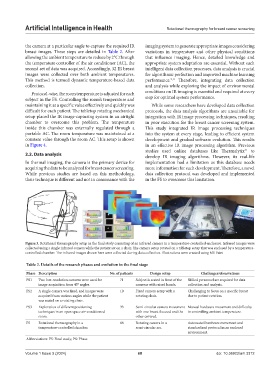
Figure 3. Rotational thermography setup in the final study consisting of an infrared camera in a temperature-controlled enclosure. Infrared images were
collected using a single infrared camera while the patient sat on a chair. The camera setup rotated on a tabletop setup that was enclosed by a temperature-
controlled chamber. The infrared images shown here were collected during data collection. Illustrations were created using MS Paint
Table 2. Details of the research phases and evolution to the final stage
Phase Description No. of patients Design setup Challenges/observations
PS1 Two low-resolution cameras were used for 71 Subject is seated in front of the Skilled personnel are required for data
image acquisition from 45° angles. cameras with raised hands. collection and analysis.
PS2 A single camera was fixed, and images were 10 Fixed camera setup with a Challenging to focus on a specific breast
acquired from various angles while the patient rotating chair. due to patient rotation.
was seated on a rotating chair.
PS3 Exploration of different positioning 33 Semi-circular camera movement Manual hardware movement and difficulty
techniques in an open space air-conditioned with one breast focused and the in controlling ambient temperature.
room. other covered.
FS Rotational thermography in a 88 Rotating camera in a Automated hardware movement and
temperature-controlled chamber. semi-circular arc. standardized protocol in an enclosed
environment.
Abbreviations: FS: Final study; PS: Phase.
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 68 doi: 10.36922/aih.3312