Page 77 - AIH-1-3
P. 77
Artificial Intelligence in Health Rotational thermography for breast cancer screening
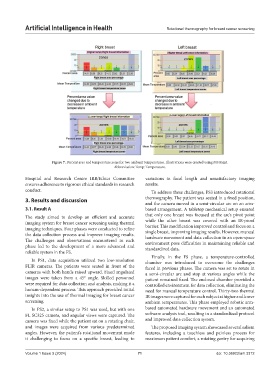
Figure 7. Percent area and temperature zone for two ambient temperatures. Illustrations were created using MS Paint.
Abbreviation: Temp: Temperature.
Hospital and Research Centre IRB/Ethics Committee variations in focal length and unsatisfactory imaging
ensures adherence to rigorous ethical standards in research results.
conduct. To address these challenges, PS3 introduced rotational
3. Results and discussion thermography. The patient was seated in a fixed position,
and the camera moved in a semi-circular arc on an arm-
3.1. Result A based arrangement. A tabletop mechanical setup ensured
The study aimed to develop an efficient and accurate that only one breast was focused at the arc’s pivot point
imaging system for breast cancer screening using thermal while the other breast was covered with an IR-proof
imaging techniques. Four phases were conducted to refine barrier. This modification improved control and focus on a
the data collection process and improve imaging results. single breast, improving imaging results. However, manual
hardware movement and data collection in an open-space
The challenges and observations encountered in each environment pose difficulties in maintaining reliable and
phase led to the development of a more advanced and standardized data.
reliable system in the FS.
Finally, in the FS phase, a temperature-controlled
In PS1, data acquisition utilized two low-resolution chamber was introduced to overcome the challenges
FLIR cameras. The patients were seated in front of the faced in previous phases. The camera was set to rotate in
cameras with both hands raised upward. Fixed angulated a semi-circular arc and stop at various angles while the
images were taken from a 45° angle. Skilled personnel patient remained fixed. The enclosed chamber provided a
were required for data collection and analysis, making it a controlled environment for data collection, eliminating the
human-dependent process. This approach provided initial need for manual temperature control. Thirty-two thermal
insights into the use of thermal imaging for breast cancer IR images were captured for each subject at higher and lower
screening. ambient temperatures. This phase employed robotic arm-
In PS2, a similar setup to PS1 was used, but with one based automated hardware movement and an automated
FL SC325 camera, and angular views were captured. The software analysis tool, resulting in a standardized protocol
camera was fixed while the patient sat on a rotating chair, and improved data collection system.
and images were acquired from various predetermined The proposed imaging system showcased several salient
angles. However, the patient’s rotational movement made features, including a touchless and painless process for
it challenging to focus on a specific breast, leading to maximum patient comfort, a rotating gantry for acquiring
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 71 doi: 10.36922/aih.3312