Page 24 - AIH-2-1
P. 24
Artificial Intelligence in Health COVID-19 diagnosis: FPA, k-NN, and SVM classifiers
COVID-19 confirmations. The proposed system achieved features promotes classification performance. Third, a
an accuracy of 94.80%. wrapper-based feature selection strategy that uses bio-
Feng et al. have proposed a predictive model using inspired algorithms is more robust and performs better
49
four classifiers, namely LR with LASSO, LR with ridge in a variety of optimization challenges when compared to
regularization, decision tree, and adaptive boosting (AB) conventional approaches to feature selection.
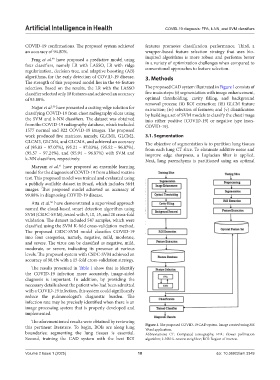
algorithms, for the early detection of COVID-19 disease. 3. Methods
The strength of this proposed model lies in the 46-feature
selection. Based on the results, the LR with the LASSO The proposed CAD system illustrated in Figure 1 consists of
classifier selected only 18 features and achieved an accuracy five main steps: (i) segmentation with image enhancement,
of 93.80%. optimal thresholding, cavity filling, and background
removal process; (ii) ROI extraction; (iii) GLCM feature
Najjar et al. have presented a cutting-edge solution for extraction; (iv) selection of features; and (v) classification
50
classifying COVID-19 from chest radiography slices using by building a set of SVM models to classify the chest image
the SVM and k-NN classifiers. The dataset was obtained into either positive (COVID-19) or negative type (non-
from the COVID-19 radiography database, which included COVID-19).
1577 normal and 822 COVID-19 images. The proposed
work produced five matrices, namely, GLCM1, GLCM2, 3.1. Segmentation
GLCM3, GLCM4, and GLCMA, and achieved an accuracy The objective of segmentation is to partition lung tissues
of (95.83 – 97.07%), (95.21 – 97.03%), (95.52 – 96.87%), from each lung CT slice. To eliminate additive noise and
(95.57 – 97.24%), and (95.94 – 96.87%) with SVM and improve edge sharpness, a Laplacian filter is applied.
k-NN classifiers, respectively. Next, lung parenchyma is partitioned using an optimal
51
Maryam et al. have proposed an ensemble learning
model for the diagnosis of COVID-19 from a blood routine
test. This proposed model was trained and evaluated using
a publicly available dataset in Brazil, which includes 5644
images. This proposed model achieved an accuracy of
99.88% in diagnosing COVID-19 disease.
Atta et al. have demonstrated a supervised approach
52
named the cloud-based smart detection algorithm using
SVM (CSDC-SVM), tested with 5, 10, 15, and 20 cross-fold
validation. The dataset included 547 samples, which were
classified using the SVM K-fold cross-validation method.
The proposed CSDC-SVM model classifies COVID-19
into four categories, namely, negative, mild, moderate,
and severe. The virus can be classified as negative, mild,
moderate, or severe, indicating its presence at various
levels. The proposed system with CSDC-SVM achieved an
accuracy of 98.4% with a 15-fold cross-validation strategy.
The results presented in Table 1 show that to identify
the COVID-19 infection more accurately, image-aided
diagnosis is important. In addition, by providing the
necessary details about the patient who had been admitted
with a COVID-19 infection, this system could significantly
reduce the pulmonologist’s diagnostic burden. The
infection rate may be precisely identified when there is an
image processing system that is properly developed and
implemented.
The aforementioned results were obtained by reviewing
this pertinent literature. To begin, ROIs are along lung Figure 1. The proposed COVID-19 CAD system. Image created using MS
Word application.
boundaries; segmenting the lung tissues is essential. Abbreviations: CT: Computed tomography; FPA: Flower pollination
Second, training the CAD system with the best ROI algorithm; k-NN: k-nearest neighbor; ROI: Region of interest.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 18 doi: 10.36922/aih.3349