Page 115 - AIH-2-3
P. 115
Artificial Intelligence in Health Opportunities for AI-based arrhythmia screening
A B
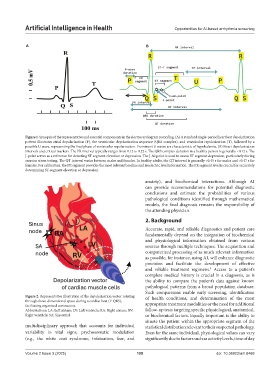
Figure 1. Synopsis of the representative and essential components in the electrocardiogram recording. (A) A standard single-period heartbeat depolarization
pattern illustrates atrial depolarization (P), the ventricular depolarization sequence (QRS complex), and ventricular repolarization (T), followed by a
possible U wave, representing the final phase of ventricular repolarization. Prominent U waves are characteristic of hypokalemia. (B) Heart depolarization
intervals and critical markers. The PR interval typically ranges from 0.12 to 0.22 s. The QRS complex duration in a healthy person is generally <0.12 s. The
J-point serves as a reference for detecting ST segment elevation or depression. The J-60 point is used to assess ST segment depression, particularly during
exercise stress testing. The QT interval varies between males and females. In healthy adults, the QT interval is generally <0.45 s for males and <0.47 s for
females. For calibration, the PR segment provides the most relevant baseline and isoelectric level information. The PR segment level is crucial for accurately
determining ST-segment elevation or depression.
anxiety), and biochemical interactions. Although AI
can provide recommendations for potential diagnostic
conclusions and estimate the probabilities of various
pathological conditions identified through mathematical
models, the final diagnosis remains the responsibility of
the attending physician.
2. Background
Accurate, rapid, and reliable diagnostics and patient care
fundamentally depend on the integration of biochemical
and physiological information obtained from various
sources through multiple techniques. The acquisition and
computerized processing of as much relevant information
as possible, for instance, using AI, will enhance diagnostic
precision and facilitate the development of effective
and reliable treatment regimens. Access to a patient’s
8
complete medical history is crucial in a diagnosis, as is
the ability to compare the patient’s data against known
pathological patterns from a broad population database.
Such comparisons enable early screening, identification
Figure 2. Representative illustration of the depolarization vector rotating of health conditions, and determination of the most
through three-dimensional space during a cardiac beat (P-QRS),
facilitating organized contraction. appropriate treatment modalities or the need for additional
Abbreviations: LA: Left atrium; LV: Left ventricle; RA: Right atrium; RV: follow-up tests targeting specific physiological, anatomical,
Right ventricle; SA: Sinoatrial. or biochemical factors. Equally important is the ability to
situate the patient within the appropriate segment of the
multidisciplinary approach that accounts for individual statistical distribution relevant to their suspected pathology.
variability in vital signs, psychosomatic modulation Even for the same individual, physiological values can vary
(e.g., the white coat syndrome, infatuation, fear, and significantly due to factors such as activity levels, time of day
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 109 doi: 10.36922/aih.8468