Page 116 - AIH-2-3
P. 116
Artificial Intelligence in Health Opportunities for AI-based arrhythmia screening
A B
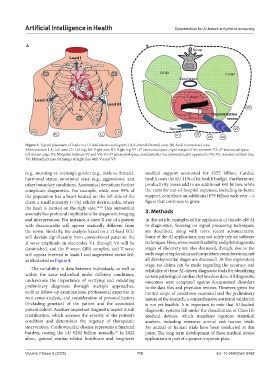
Figure 3. Typical placement of leads in a 12-lead electrocardiogram. (A) Coronal (frontal) view. (B) Axial (transverse) view
th
Abbreviations: LA: Left arm; LL: Left leg; RA: Right arm; RL: Right leg; V1: 4 intercostal space, right margin of the sternum; V2: 4 intercostal space,
th
th
left sternal edge; V3: Midpoint between V2 and V4; V4: 5 intercostal space, midclavicular line (symmetrically opposed to V2; V5: Anterior axillary line;
V6: Midaxillary line, forming a straight line with V4 and V5.
(e.g., morning vs. evening), gender (e.g., male vs. female), medical support accounted for €155 billion. Cardiac
hormonal status, emotional state (e.g., aggression), and health costs the EU 11% of its health budget. Furthermore,
other boundary conditions. Anatomical deviations further productivity losses add in an additional €48 billion, while
complicate diagnostics. For example, while over 99% of the costs for out-of-hospital expenses, including in-home
the population has a heart located on the left side of the support, contribute an additional €79 billion each year – a
chest, a small minority (<1%) exhibit dextrocardia, where figure that continues to grow.
the heart is located on the right side. 16-18 This anatomical
anomaly has profound implications for diagnostic imaging 3. Methods
and interpretation. For instance, a chest X-ray of a patient In this article, examples of the application of decade-old AI
with dextrocardia will appear markedly different from in diagnostics, focusing on signal processing techniques,
the norm. Similarly, the analysis based on a 12-lead ECG are described, along with more recent advancements.
will deviate significantly from conventional patterns: the Some of the AI applications may not solely rely on software
R wave amplitude in electrodes V1 through V6 will be techniques. Here, some recent feasibility and pilot diagnostic
diminished, and the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave stages of discovery are also discussed, though, due to the
will appear inverted in leads I and augmented vector left, early stage of exploration and proprietary considerations, not
as illustrated in Figure 4. all developmental stages are discussed. At this exploratory
stage, no claims can be made regarding the accuracy and
The variability in data between individuals, as well as reliability of these AI-driven diagnostic tools for identifying
within the same individual under different conditions, certain pathological cardiac rhythm disorders. All diagnostic
underscores the importance of verifying and validating outcomes were compared against documented disorders
preliminary diagnoses through multiple approaches, in the data files and physician reviews. However, given the
such as follow-up examinations, professional expertise in limited scope of conditions examined and the preliminary
root-cause analysis, and consideration of personal history nature of the research, a comprehensive statistical validation
(including genetics) of the patient and the associated is not yet feasible. It is important to note that AI-backed
patient cohort. Another important diagnostic aspect is risk diagnostic systems fall under the classification of Class IIb
stratification, which assesses the severity of the patient’s medical devices, which mandates rigorous statistical
condition and determines the urgency of therapeutic analysis, including extensive animal and human trials.
intervention. Cardiovascular disease represents a financial No animal or human trials have been conducted at this
19
burden, costing the EU €282 billion annually. In 2022 point. The long-term development of these medical device
alone, general cardiac-related healthcare and long-term applications is part of a greater corporate plan.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 110 doi: 10.36922/aih.8468