Page 90 - AIH-2-4
P. 90
Artificial Intelligence in Health Federated learning health stack against pandemics
90.0% in classifying smart contract vulnerabilities. The real-world medical datasets and can therefore be used as
model’s performance was evaluated using various metrics, a reliable data proxy. MNIST consists of 70,000 grayscale
including precision, recall, F1 score, confusion matrix, and images, with 60,000 images used for training and 10,000
receiver operating characteristic curves, demonstrating for testing. Each image is 28 × 28 pixels and encoded with
its effectiveness in detecting vulnerabilities compared to intensity values ranging from 0 to 255.
random guessing. For model training, a CNN architecture was designed
3. Results with an input layer, two hidden layers activated by ReLU
functions, and an output layer generating a probability
In this section, the cost-effectiveness and performance of distribution over 10 classes using a softmax function. The
the proposed hierarchical FL framework were theoretically model was trained for 30 communication rounds. In the
and experimentally analyzed. The analyses considered baseline FedAvg setup, the simulation involved 12 and
both communication costs and computation costs for all 21 clients and a single central server. For the hierarchical
entities involved in the training process: Clients, local FL implementation, two configurations were tested:
servers, and the central server. To demonstrate the utility first, with four local servers, each connected to three
of the proposed framework, the observed accuracy was client nodes (totaling 12 nodes, matching the first non-
compared with the benchmark FL algorithm, FedAvg, hierarchical case), and one central server coordinating the
53
with fine-tuning. aggregation; second, with three local servers and seven
clients per server (totaling 21 nodes, corresponding to the
3.1. Experimental evaluation
second non-hierarchical case), and a central server. The
The experiments were conducted using the structure learning rate was set to 0.01, and each client performed
of Flower Framework, extended to support both a three local training epochs per round. Throughout the
54
standard FedAvg setup and the proposed hierarchical FL training process, both training time and accuracy at each
framework. Python 3.10.12 (Phyton software foundation, round were monitored to compare model performance.
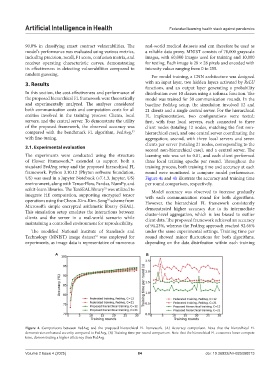
US) was used in a Jupyter Notebook (v7.4.3, Jupyter, US) Figure 4a and 4b illustrate the accuracy and training time
environment, along with TensorFlow, Pandas, NumPy, and per round comparison, respectively.
scikit-learn libraries. The TenSEAL library was utilized to Model accuracy was observed to increase gradually
55
integrate HE computation, supporting encrypted tensor with each communication round for both algorithms.
operations using the Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song scheme from However, the hierarchical FL framework consistently
56
Microsoft’s simple encrypted arithmetic library (SEAL). demonstrated higher accuracy due to its intermediate
This simulation setup emulates the interactions between cluster-level aggregation, which is less biased to outlier
clients and the server in a real-world scenario while client data. The proposed framework achieved an accuracy
maintaining a controlled environment for reproducibility. of 94.23%, whereas the FedAvg approach reached 92.66%
The modified National Institute of Standards and under the same experimental settings. Training time per
Technology (MNIST) image dataset was employed for round showed minor fluctuations for both algorithms,
57
experiments, as image data is representative of numerous depending on the data distribution within each training
A B
Figure 4. Comparisons between FedAvg and the proposed hierarchical FL framework. (A) Accuracy comparison. Note that the hierarchical FL
demonstrates enhanced security compared to FedAvg. (B) Training time per round comparison. Note that the hierarchical FL consumes lesser compute
time, demonstrating a higher efficiency than FedAvg.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 84 doi: 10.36922/AIH025080013