Page 96 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 96
Fan, et al.
were used to generate the comprehensive suitability Hydrogeologically, the aquifer in this region consists
map, which was then classified into zones according to of alluvial sand and gravel with diverse lithological
the integrated scoring classification standard. The final compositions and interbedded low-permeability layers,
suitability zoning of water source intake sites in the such as fine sand and silt. The average permeability
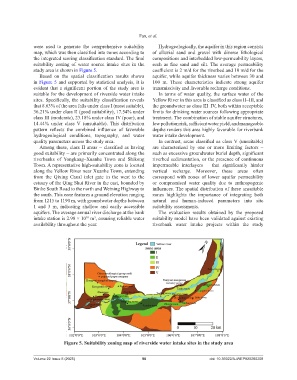
study area is shown in Figure 5. coefficient is 2 m/d for the riverbed and 10 m/d for the
Based on the spatial classification results shown aquifer, while aquifer thickness varies between 30 and
in Figure 5 and supported by statistical analysis, it is 100 m. These characteristics indicate strong aquifer
evident that a significant portion of the study area is transmissivity and favorable recharge conditions.
suitable for the development of riverside water intake In terms of water quality, the surface water of the
sites. Specifically, the suitability classification reveals Yellow River in this area is classified as class II–III, and
that 8.63% of the area falls under class I (most suitable), the groundwater as class III–IV, both within acceptable
36.21% under class II (good suitability), 17.54% under limits for drinking water sources following appropriate
class III (moderate), 23.18% under class IV (poor), and treatment. The combination of stable aquifer structures,
14.44% under class V (unsuitable). This distribution low pollution risk, sufficient water yield, and manageable
pattern reflects the combined influence of favorable depths renders this area highly favorable for riverbank
hydrogeological conditions, topography, and water water intake development.
quality parameters across the study area. In contrast, areas classified as class V (unsuitable)
Among these, class II areas – classified as having are characterized by one or more limiting factors –
good suitability – are primarily concentrated along the such as excessive groundwater burial depth, significant
riverbanks of Yongkang–Xuanhe Town and Shikong riverbed sedimentation, or the presence of continuous
Town. A representative high-suitability zone is located impermeable interlayers – that significantly hinder
along the Yellow River near Xuanhe Town, extending vertical recharge. Moreover, these areas often
from the Qixing Canal inlet gate in the west to the correspond with zones of lower aquifer permeability
estuary of the Qing Shui River in the east, bounded by or compromised water quality due to anthropogenic
Binhe South Road to the north and Weining Highway to influences. The spatial distribution of these unsuitable
the south. This zone features a ground elevation ranging zones highlights the importance of integrating both
from 1215 to 1190 m, with groundwater depths between natural and human-induced parameters into site
1 and 3 m, indicating shallow and easily accessible suitability assessments.
aquifers. The average annual river discharge at the bank The evaluation results obtained by the proposed
intake station is 2.98 × 10 m , ensuring reliable water suitability model have been validated against existing
3
10
availability throughout the year. riverbank water intake projects within the study
Figure 5. Suitability zoning map of riverside water intake sites in the study area
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 90 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025260208