Page 97 - AJWEP-22-5
P. 97
Evaluation of riverbank water suitability
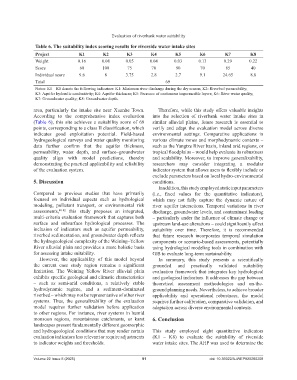
Table 6. The suitability index scoring results for riverside water intake sites
Project K1 K2 K3 K4 K5 K6 K7 K8
Weight 0.16 0.08 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.13 0.29 0.22
Score 60 100 75 70 90 70 85 40
Individual score 9.6 8 3.75 2.8 2.7 9.1 24.65 8.8
Total 69
Notes: K1 – K8 denote the following indicators: K1: Minimum river discharge during the dry season; K2: Riverbed permeability;
K3: Aquifer hydraulic conductivity; K4: Aquifer thickness; K5: Presence of continuous impermeable layers; K6: River water quality;
K7: Groundwater quality; K8: Groundwater depth.
area, particularly the intake site near Xuanhe Town. Therefore, while this study offers valuable insights
According to the comprehensive index evaluation into the selection of riverbank water intake sites in
(Table 6), this site achieves a suitability score of 69 similar alluvial plains, future research is essential to
points, corresponding to a class II classification, which verify and adapt the evaluation model across diverse
indicates good exploitation potential. Field-based environmental settings. Comparative applications in
hydrogeological surveys and water quality monitoring various climate zones and morphodynamic contexts –
data further confirm that the aquifer thickness, such as the Yangtze River basin, inland arid regions, or
permeability, water depth, and surface–groundwater tropical floodplains – would help evaluate its robustness
quality align with model predictions, thereby and scalability. Moreover, to improve generalizability,
demonstrating the practical applicability and reliability researchers may consider integrating a modular
of the evaluation system. indicator system that allows users to flexibly include or
exclude parameters based on local hydro-environmental
5. Discussion conditions.
In addition, this study employed static input parameters
Compared to previous studies that have primarily (i.e., fixed values for the quantitative indicators),
focused on individual aspects such as hydrological which may not fully capture the dynamic nature of
modeling, pollutant transport, or environmental risk river–aquifer interactions. Temporal variations in river
assessments, 40-42 this study proposes an integrated, discharge, groundwater levels, and contaminant loading
multi-criteria evaluation framework that captures both – particularly under the influence of climate change or
surface and subsurface hydrological processes. The upstream land-use alterations – could significantly affect
inclusion of indicators such as aquifer permeability, suitability over time. Therefore, it is recommended
riverbed sedimentation, and groundwater depth reflects that future research incorporates temporal simulation
the hydrogeological complexity of the Weining–Yellow components or scenario-based assessments, potentially
River alluvial plain and provides a more holistic basis using hydrological modeling tools in combination with
for assessing intake suitability. GIS to evaluate long-term sustainability.
However, the applicability of this model beyond In summary, this study presents a scientifically
the current case study region remains a significant grounded and practically validated suitability
limitation. The Weining–Yellow River alluvial plain evaluation framework that integrates key hydrological
exhibits specific geological and climatic characteristics and geological indicators. It addresses the gap between
– such as semi-arid conditions, a relatively stable theoretical assessment methodologies and on-the-
hydrodynamic regime, and a sediment-dominated ground planning needs. Nevertheless, to achieve broader
riverbed – which may not be representative of other river applicability and operational robustness, the model
systems. Thus, the generalizability of the evaluation requires further calibration, comparative validation, and
model requires further validation before application adaptation across diverse environmental contexts.
to other regions. For instance, river systems in humid
monsoon regions, mountainous catchments, or karst 6. Conclusion
landscapes present fundamentally different geomorphic
and hydrogeological conditions that may render certain This study employed eight quantitative indicators
evaluation indicators less relevant or require adjustments (K1 – K8) to evaluate the suitability of riverside
to indicator weights and thresholds. water intake sites. The AHP was used to determine the
Volume 22 Issue 5 (2025) 91 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025260208