Page 75 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 75
Flood risk assessment of Barak river valley
A B
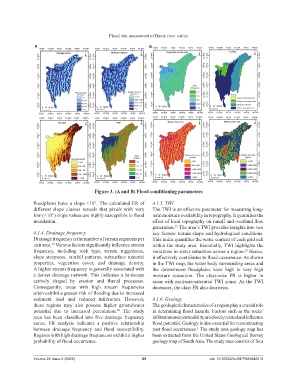
Figure 3. (A and B) Flood conditioning parameters
floodplains have a slope <10°. The calculated FR of 4.1.5. TWI
different slope classes reveals that pixels with very The TWI is an effective parameter for measuring long-
low (<10°) slope values are highly susceptible to flood term moisture availability in topography. It quantifies the
inundation. effect of local topography on runoff and overland flow
generation. The area’s TWI provides insights into two
35
4.1.4. Drainage frequency key factors: terrain shape and hydrological conditions.
Drainage frequency is the number of stream segments per This index quantifies the water content of each grid cell
unit area. Various factors significantly influence stream within the study area. Essentially, TWI highlights the
32
frequency, including rock type, terrain ruggedness, variations in water saturation across a region. Hence,
33
slope steepness, rainfall patterns, subsurface material it effectively contributes to flood occurrence. As shown
properties, vegetation cover, and drainage density. in the TWI map, the water body surrounding areas and
A higher stream frequency is generally associated with the downstream floodplains have high to very high
a denser drainage network. This indicates a landscape moisture saturation. The class-wise FR is higher in
actively shaped by erosion and fluvial processes. areas with moisture-saturated TWI zones. As the TWI
Consequently, areas with high stream frequencies decreases, the class FR also decreases.
often exhibit a greater risk of flooding due to increased
sediment load and reduced infiltration. However, 4.1.6. Geology
these regions may also possess higher groundwater The geological characteristics of a region play a crucial role
potential due to increased percolation. The study in determining flood hazards. Factors such as the rocks’
34
area has been classified into five drainage frequency infiltration and permeability are closely related and influence
zones. FR analysis indicates a positive relationship flood potential. Geology is also essential for reconstructing
between drainage frequency and flood susceptibility. past flood occurrences. The study area geology map has
4
Regions with high drainage frequencies exhibit a higher been extracted from the United States Geological Survey
probability of flood occurrence. geology map of South Asia. The study area consists of four
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 69 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025040019