Page 54 - AN-1-1
P. 54
Advanced Neurology EPAC2 null leads to tauopathy
somatodendritic compartment of CA1 and CA3 neurons in using a previously reported protocol . In the RIPA
[20]
EPAC2 mice (Figure 1L-O). To exclude the involvement fraction (soluble tau), only slight increases in pT231 and
−/−
of developmental factors in tau phosphorylation, we pT205/pT231 were found in the EPAC2 mice on the
−/−
transfected short hairpin RNA (shRNA) toward mouse 6 and 18 months, respectively (Figure 3A-D). However,
th
th
EPAC2 into N2a cells and examined tau phosphorylation at immunoactivity toward phosphorylated tau (pT205,
these sites. In line with our in vivo data, silencing of EPAC2 pT231, pS396, and pS404) in the 70% FA fraction (insoluble
led to the hyperphosphorylation of tau at multiple epitopes tau) was dramatically increased in EPAC2 mice,
−/−
(Figure 1J and K). We next examined whether EPAC2 especially in the 18-month-old mice (Figure 3E-H). Thus,
expression was reduced in the transgenic AD mouse model. loss of EPAC2 decreases the solubility of tau and promotes
By RT-PCR and Western blot, both the mRNA and protein its aggregation. Because the aggregation of tau is one of
levels of EPAC2 were reduced in the hippocampus of Tg2576 the key steps in the formation of NFTs, we then performed
mice on the 12 month (Figure 1A-D). Moreover, the Bielschowsky silver staining to visualize the morphology
th
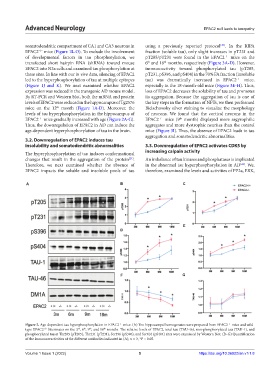
levels of tau hyperphosphorylation in the hippocampus of of neurons. We found that the cortical neurons in the
EPAC2 mice gradually increased with age (Figure 2A-G). EPAC2 mice (9 month) displayed more argyrophilic
−/−
th
−/−
Thus, the downregulation of EPAC2 in AD can induce the aggregates and more dystrophic neurites than the control
age-dependent hyperphosphorylation of tau in the brain. mice (Figure 3I). Thus, the absence of EPAC2 leads to tau
aggregation and somatodendritic abnormalities.
3.2. Downregulation of EPAC2 induces tau
insolubility and somatodendritic abnormalities 3.3. Downregulation of EPAC2 activates CDK5 by
The hyperphosphorylation of tau induces conformational increasing calpain activity
changes that result in the aggregation of the protein . An imbalance of tau kinases and phosphatases is implicated
[21]
Therefore, we next examined whether the absence of in the abnormal tau hyperphosphorylation in AD . We,
[22]
EPAC2 impacts the soluble and insoluble pools of tau therefore, examined the levels and activities of PP2a, ERK,
A B C
E
D
F G
Figure 2. Age-dependent tau hyperphosphorylation in EPAC2 mice. (A) The hippocampal homogenates were prepared from EPAC2 mice and wild-
−/−
−/−
rd
+/+
type EPAC2 littermates on the 3 , 6 , 9 , and 18 months. The relative levels of EPAC2, total tau (TAU-46), non-phosphorylated tau (TAU-1), and
th
th
th
phosphorylated tau at Thr205 (pT205), Thr231 (pT231), Ser396 (pS396), and Ser404 (pS404) sites were examined by Western blot. (B–G) Quantification
of the immunoreactivities of the different antibodies indicated in (A); n = 3, *P < 0.05.
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i1.8