Page 56 - AN-1-1
P. 56
Advanced Neurology EPAC2 null leads to tauopathy
A B C D
E F
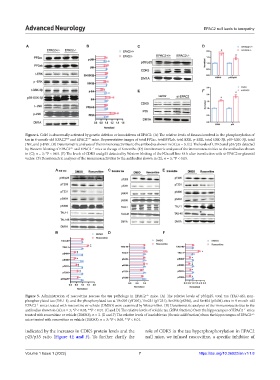
Figure 4. Cdk5 is abnormally activated by genetic deletion or knockdown of EPAC2. (A) The relative levels of kinases involved in the phosphorylation of
tau in 6-month-old EPAC2 and EPAC2 mice. Representative images of total PP2ac, total PP2ab, total ERK, p-ERK, total GSK-3β, pS9-GSK-3β, total
+/+
−/−
JNK, and p-JNK. (B) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown in (A); n = 3. (C) The levels of CDK5 and p35/p25 detected
by Western blotting of EPAC2 and EPAC2 mice at the age of 6 months. (D) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown
+/+
−/−
in (C); n = 3; *P < 0.05. (E) The levels of CDK5 and p35 detected by Western blotting of the N2a cell line 48 h after transfection with si-EPAC2 or plasmid
vector. (F) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown in (E); n = 3; *P < 0.05.
A C E
B D F
Figure 5. Administration of roscovitine rescues the tau pathology in EPAC2 mice. (A) The relative levels of p35/p25, total tau (TAU-46), non-
−/−
phosphorylated tau (TAU-1), and the phosphorylated tau at Thr205 (pT205), Thr231 (pT231), Ser396 (pS396), and Ser404 (pS404) sites in 9-month-old
EPAC2 mice treated with roscovitine or vehicle (DMSO) were examined by Western blot. (B) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the
−/−
antibodies shown in (A); n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (C and D) The relative levels of soluble tau (RIPA fraction) from the hippocampus of EPAC2 mice
−/−
treated with roscovitine or vehicle (DMSO); n = 3. (E and F) The relative levels of insoluble tau (formic acid fraction) from the hippocampus of EPAC2
−/−
mice treated with roscovitine or vehicle (DMSO); n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
indicated by the increases in CDK5 protein levels and the role of CDK5 in the tau hyperphosphorylation in EPAC2
p25/p35 ratio (Figure 4E and F). To further clarify the null mice, we infused roscovitine, a specific inhibitor of
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i1.8