Page 57 - AN-1-1
P. 57
Advanced Neurology EPAC2 null leads to tauopathy
A B C
D E F G
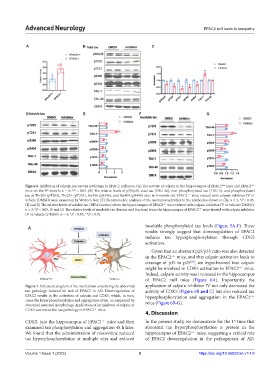
Figure 6. Inhibition of calpain rescues tau pathology in EPAC2 null mice. (A) The activity of calpain in the hippocampus of EPAC2 mice and EPAC2
+/+
−/−
mice on the 9 month; n = 6; *P < 0.05. (B) The relative levels of p35/p25, total tau (TAU-46), non-phosphorylated tau (TAU-1), and phosphorylated
th
tau at Thr205 (pT205), Thr231 (pT231), Ser396 (pS396), and Ser404 (pS404) sites in 9-month-old EPAC2 mice treated with calpain inhibitor IV or
−/−
vehicle (DMSO) were examined by Western blot. (C) Densitometric analyses of the immunoreactivities to the antibodies shown in (B); n = 3, *P < 0.05.
(D and E) The relative levels of soluble tau (RIPA fraction) from the hippocampus of EPAC2 mice treated with calpain inhibitor IV or vehicle (DMSO);
−/−
n = 3; *P < 0.05. (F and G) The relative levels of insoluble tau (formic acid fraction) from the hippocampus of EPAC2 mice treated with calpain inhibitor
−/−
IV or vehicle (DMSO). n = 3; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
insoluble phosphorylated tau levels (Figure 5A-F). These
results strongly suggest that downregulation of EPAC2
induces tau hyperphosphorylation through CDK5
activation.
Given that an aberrant p25/p35 ratio was also detected
in the EPAC2 mice, and that calpain activation leads to
−/−
[23]
cleavage of p35 to p25 , we hypothesized that calpain
might be involved in CDK5 activation in EPAC2 mice.
−/−
Indeed, calpain activity was increased in the hippocampus
of EPAC2 null mice (Figure 6A). Importantly, the
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the mechanism underlying the abnormal application of calpain inhibitor IV not only decreased the
tau pathology induced by lack of EPAC2 in AD. Downregulation of activity of CDK5 (Figure 6B and C) but also reduced tau
EPAC2 results in the activation of calpain and CDK5, which, in turn, hyperphosphorylation and aggregation in the EPAC2
−/−
cause the hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau, accompanied by mice (Figure 6B-G).
abnormal neuronal morphology. Application of an inhibitor of calpain or
−/−
CDK5 can rescue the tau pathology in EPAC2 mice.
4. Discussion
CDK5, into the hippocampus of EPAC2 mice and then In the present study, we demonstrate for the 1 time that
st
−/−
examined tau phosphorylation and aggregation 48 h later. abnormal tau hyperphosphorylation is present in the
We found that the administration of roscovitine reduced hippocampus of EPAC2 mice, suggesting a critical role
−/−
tau hyperphosphorylation at multiple sites and reduced of EPAC2 downregulation in the pathogenesis of AD.
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i1.8