Page 24 - AN-1-3
P. 24
Advanced Neurology Early inhibition of PDK1 prevents AD-like pathology
A B
C
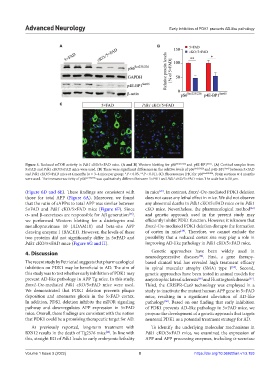
Figure 5. Reduced mTOR activity in Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice. (A and B) Western blotting for pS6 Ser235/236 and p4E-BP1 Ser65 . (A) Cortical samples from
5×FAD and Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice were used. (B) There were significant differences in the relative levels of pS6 Ser235/236 and p4E-BP1 Ser65 between 5×FAD
and Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice at 4 months (n = 3–4 mice per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (C) Fluorescence IHC for pS6 Ser235/236 . Brain sections at 4 months
were used. The immunoreactivity of pS6 Ser235/236 was qualitatively different between 5×FAD and Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice. The scale bar is 50 μm.
(Figure 6D and 6E). These findings are consistent with in mice . In contrast, Emx1-Cre-mediated PDK1 deletion
[27]
those for total APP (Figure 6A). Moreover, we found does not cause any lethal effect in mice. We did not observe
that the ratio of sAPPα to total APP was similar between any abnormal deaths in Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice or in Pdk1
5×FAD and Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice (Figure 6F). Since cKO mice. Nevertheless, the pharmacological method
[22]
α- and β-secretases are responsible for Aβ generation , and genetic approach used in the present study may
[53]
we performed Western blotting for a disintegrin and efficiently inhibit PDK1 function. However, it is known that
metalloproteinase 10 (ADAM10) and beta-site APP Emx1-Cre-mediated PDK1 deletion disrupts the formation
cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1). However, the levels of these of cortex in mice . Therefore, we cannot exclude the
[28]
two proteins did not significantly differ in 5×FAD and possibility that a reduced cortex size may play a role in
Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice (Figure 6G and H). improving AD-like pathology in Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice.
4. Discussion Genetic approaches have been widely used in
neurodegenerative diseases . First, a gene therapy-
[54]
The recent study by Petri et al. suggests that pharmacological based clinical trial has revealed high treatment efficacy
inhibition on PDK1 may be beneficial to AD. The aim of in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) type 1 . Second,
[55]
this study was to test whether early inhibition of PDK1 may genetic approaches have been tested in animal models for
prevent AD-like pathology in APP Tg mice. In this study, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Huntington’s disease .
[57]
[56]
Emx1-Cre-mediated Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice were used. Third, the CRISPR-Cas9 technology was employed in a
We demonstrated that PDK1 deletion prevents plaque study to inactivate the mutant human APP gene in 5×FAD
deposition and attenuates gliosis in the 5×FAD cortex. mice, resulting in a significant alleviation of AD-like
In addition, PDK1 deletion inhibits the mTOR signaling pathology . Based on our finding that early inhibition
[58]
pathway and downregulates APP expression in 5×FAD of PDK1 prevents AD-like pathology in 5×FAD mice, we
mice. Overall, these findings are consistent with the notion propose the development of a genetic approach that targets
that PDK1 could be a promising therapeutic target for AD. neuronal PDK1 as a potential treatment strategy for AD.
As previously reported, long-term treatment with To identify the underlying molecular mechanisms in
BX912 results in the death of Tg2576 mice . In line with Pdk1 cKO/5×FAD mice, we examined the expression of
[22]
this, straight KO of Pdk1 leads to early embryonic lethality APP and APP processing enzymes, including α-secretase
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i3.153