Page 34 - AN-2-4
P. 34
Advanced Neurology Evoked potential response in parkinsonian syndromes
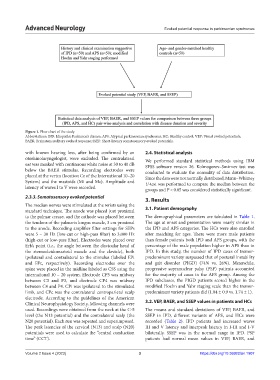
Figure 1. Flow chart of the study.
Abbreviations: IPD: Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease; APS: Atypical parkinsonian syndromes; HC: Healthy control; VEP: Visual evoked potentials;
BAER: Brainstem auditory evoked response; SSEP: Short-latency somatosensory evoked potentials.
with known hearing loss, after being confirmed by an 2.4. Statistical analysis
otorhinolaryngologist, were excluded. The contralateral We performed standard statistical methods using IBM
ear was masked with continuous white noise at 30 to 40 dB SPSS software version 26. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was
below the BAER stimulus. Recording electrodes were conducted to evaluate the normality of data distribution.
placed at the vertex (location Cz of the International 10–20 Since the data were not normally distributed, Mann–Whitney
System) and the mastoids (Mi and Mc). Amplitude and U-test was performed to compare the median between the
latency of waves I to V were recorded. groups and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.3.3. Somatosensory evoked potential 3. Results
The median nerves were stimulated at the wrists using the
standard technique. The anode was placed just proximal 3.1. Patient demography
to the palmar crease, and the cathode was placed between The demographical parameters are tabulated in Table 1.
the tendons of the palmaris longus muscle, 3 cm proximal The age at onset and presentation were nearly similar in
to the anode. Recording amplifier filter settings for SEPs the IPD and APS categories. The HCs were also enrolled
were 5 – 30 Hz (low-cut or high-pass filter) to 3,000 Hz after matching for ages. There were more male patients
(high-cut or low-pass filter). Electrodes were placed over than female patients both IPD and APS groups, with the
Erb’s point (i.e., the angle between the clavicular head of percentage of the male population higher in APS than in
the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the clavicle), both IPD. In this study, the number of IPD cases of tremor-
ipsilateral and contralateral to the stimulus (labeled EPi predominant variety surpassed that of postural instability
and EPc, respectively). Recording electrodes over the and gait disorder (PIGD) (74% vs. 26%). Meanwhile,
spine were placed in the midline labeled as C5S using the progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) patients accounted
international 10 – 20 system. Electrode CP3 was midway for the majority of cases in the APS group. Among the
between C3 and P3, and electrode CP4 was midway IPD subclasses, the PIGD patients scored higher in the
between C4 and P4. CPi was ipsilateral to the stimulated modified Hoehn and Yahr staging scale than the tremor-
limb, and CPc was the contralateral centroparietal scalp predominant variety patients did (1.84 ± 0.9 vs. 1.74 ± 1).
electrode. According to the guidelines of the American
Clinical Neurophysiology Society, following channels were 3.2. VEP, BAER, and SSEP values in patients and HCs
used. Recordings were obtained from the neck at the C-5 The means and standard deviations of VEP, BAER, and
level (the N13 potential) and the contralateral scalp (the SSEP in IPD, different variants of APS, and HCs were
N20 potential). Each run was repeated and superimposed. recorded (Table 2). IPD patients had increased waves
The peak latencies of the cervical (N13) and scalp (N20) III and V latency and interpeak latency in I-III and I-V
potentials were used to calculate the “central conduction bilaterally. SSEP was in the normal range in IPD. PSP
time” (CCT). patients had normal mean values in VEP, BAER, and
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1907