Page 35 - AN-2-4
P. 35
Advanced Neurology Evoked potential response in parkinsonian syndromes
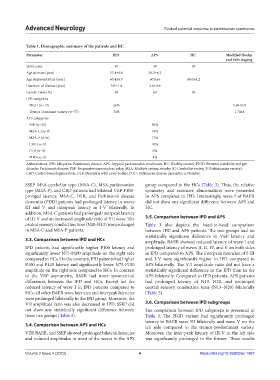
Table 1. Demographic summary of the patients and HC
Parameter IPD APS HC Modified Hoehn
and Yahr staging
Total cases 50 50 50
Age at onset (year) 57.4±6.8 58.2±6.2
Age at presentation (year) 60.4±6.9 60.8±6 60.0±4.2
Duration of disease (year) 3.0±1.4 2.6±0.8
Gender (male %) 58 64 50
IPD categories
PIGD (n=13) 26% 1.84±0.9
Tremor-dominant variety (n=37) 74% 1.74±1
APS categories
PSP (n=25) 50%
MSA-C (n=9) 18%
MSA-P (n=6) 12%
CBD (n=5) 10%
DLB (n=3) 6%
PDD (n=2) 4%
Abbreviations: IPD: Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease; APS: Atypical parkinsonian syndromes; HC: Healthy control; PIGD: Postural instability and gait
disorder Parkinson’s disease; PSP: Progressive supranuclear palsy; MSA: Multiple system atrophy (C: Cerebellar variety, P: Parkinsonian variety);
CBD: Corticobasal degeneration; DLB: Dementia with Lewy bodies; PDD: Parkinson’s disease dementia; n: Number.
SSEP. MSA-cerebellar type (MSA-C), MSA-parkinsonian group compared to the HCs (Table 3). Thus, the relative
type (MSA-P), and CBD patients had bilateral VEP P100- symmetry and extensive abnormalities were presented
pronged latency. MSA-C, DLB, and Parkinson’s disease in APS compared to IPD. Interestingly, wave I of BAER
dementia (PDD) patients had prolonged latency in waves did not show any significant difference between APS and
III and V and interpeak latency in I-V bilaterally. In HC.
addition, MSA-C patients had prolonged interpeak latency
of III-V and an increased amplitude ratio of V/I wave. The 3.5. Comparison between IPD and APS
central sensory conduction time (N20-N13) was prolonged Table 3 also depicts the head-to-head comparison
in MSA-C and MSA-P patients. between IPD and APS patients. The two groups had no
statistically significant difference in VEP latency and
3.3. Comparison between IPD and HCs amplitude. BAER showed reduced latency of wave I and
IPD patients had significantly higher P100 latency and prolonged latency of waves II, II, IV, and V on both sides
significantly lower N75-P100 amplitude on the right side in IPD compared to APS. The interpeak latencies of I-III
compared to HCs. On the contrary, IPD patients had higher and I-V were significantly higher in IPD compared to
P100 and P145 latency and significantly lower N75-P100 APS bilaterally. The V/I amplitude ratio did not have a
amplitude on the right side compared to HCs. In contrast statistically significant difference in the IPD than in the
to the VEP asymmetry, BAER had more symmetrical APS bilaterally. Compared to IPD patients, APS patients
differences between the IPD and HCs. Except for the had prolonged latency of N13, N20, and prolonged
reduced latency of wave I in IPD patients compared to central sensory conduction time (N13–N20) bilaterally
HCs, all other BAER wave latencies and interpeak latencies (Table 3).
were prolonged bilaterally in the IPD group. Moreover, the
V/I amplitude ratio was also decreased in IPD. SSEP did 3.6. Comparison between IPD subgroups
not show any statistically significant difference between The comparison between IPD subgroups is presented in
these two groups (Table 3). Table 3. The PIGD variant had significantly prolonged
latency in BAER wave III bilaterally and wave V on the
3.4. Comparison between APS and HCs left side compared to the tremor-predominant variety.
VEP, BAER, and SSEP showed prolonged bilateral latencies Moreover, the inter-peak latency of III-V in the left side
and reduced amplitudes in most of the waves in the APS was significantly prolonged in the former. These results
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1907