Page 60 - AN-2-4
P. 60
Advanced Neurology Genomic insights into Alzheimer
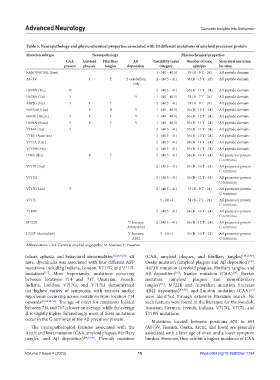
Table 5. Neuropathology and physicochemical properties associated with 20 different mutations of amyloid precursor protein
Mutation subtype Neuropathology Physicochemical properties
CAA Amyloid Fibrillary Aß Instability index Number of toxic Structural mutation
present plaques tangles deposition category epitopes location
KM670/671NL (Swe) 1 - (40 – 40.5) 33 (B - 9 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
A673V Y Y Y-cerebellum 2 - (40.5 – 41) 36 (B - 13 T - 23) Aß peptide domain
only
D678N (Tot) N 2 - (40.5 – 41) 35 (B - 11 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
D678H (Tai) Y Y 1 - (40 – 40.5) 31 (B - 7 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
A692G (Fle) Y Y Y 2 - (40.5 – 41) 33 (B - 9 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
E693Del (Osa) Y N Y 1 - (40 – 40.5) 36 (B - 12 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
E693G (Arctic) Y Y Y Y 1 - (40 – 40.5) 36 (B - 12 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
D694N (Iowa) Y Y Y Y 1 - (40 – 40.5) 35 (B - 11 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
T714A (Ira) Y 2 - (40.5 – 41) 35 (B - 11 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
T714I (Austrian) 2 - (40.5 – 41) 36 (B - 12 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
V715A (Ger) 2 - (40.5 – 41) 38 (B - 14 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
V715M (Fre) 2 - (40.5 – 41) 35 (B - 11 T - 24) Aß peptide domain
I716F (Ibe) Y Y 2 - (40.5 – 41) 34 (B - 10 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
C-terminus
V717F (Ind) 2 - (40.5 – 41) 34 (B - 10 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
C-terminus
V717G 2 - (40.5 – 41) 36 (B - 12 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
C-terminus
V717I (Lon) Y 2 - (40.5 – 41) 33 (B - 9 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
C-terminus
V717L 3 - (41+) 31 (B - 7 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
C-terminus
T719N 2 - (40.5 – 41) 34 (B - 10 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
C-terminus
M722K Y-Increase 2 - (40.5 – 41) 36 (B - 12 T - 24) Aß precursor protein
Aß40/Aß42 C-terminus
L723P (Australian) Y-Increase 3 - (41+) 33 (B - 10 T - 23) Aß precursor protein
Aß42 C-terminus
Abbreviations: CAA: Cerebral amyloid angiopathy; N: Absence; Y: Presence.
failure, aphasia, and behavioral abnormalities [11,14,51,52] . Of (CAA, amyloid plaques, and fibrillary tangles) [14,15,49] ,
[18]
note, dyscalculia was associated with four different APP Osaka mutation (amyloid plaques and Aβ deposition) ,
mutations, including Indiana, London, V717G, and V717L A673V mutation (amyloid plaques, fibrillary tangles, and
mutations . More importantly, mutations occurring Aβ deposition) , Iranian mutation (CAA) , Iberian
[14]
[16]
[15]
between locations 714 and 717 (Austrian, French, mutation (amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary
Indiana, London, V717G, and V717L) demonstrated tangles) , M722K and Australian mutation (increase
[55]
the highest variety of symptoms, with seizures and/or Aβ42 deposition) [54,56] , and London mutation (CAA)
[14]
myoclonus occurring across mutations from location 714 were identified through extensive literature search. No
onwards [15,50,52-54] . The age of onset for mutations located such features were found in the literature for the Swedish,
between 714 and 717 is lower on average, while the average Austrian, German, French, Indiana, V717G, V717L, and
II is slightly higher. Interestingly, most of these mutations T719N mutations.
occur in the C-terminus of the Aβ precursor protein.
Mutations located between positions 670 to 694
The neuropathological features associated with the (A673V, Flemish, Osaka, Arctic, and Iowa) are generally
Arctic and Iowa mutation (CAA, amyloid plaques, fibrillary associated with a later age of onset and a lower symptom
tangles, and Aβ deposition) [14,15,49] , Flemish mutation burden. However, they exhibit a higher incidence of CAA
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 15 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1734