Page 55 - AN-2-4
P. 55
Advanced Neurology Genomic insights into Alzheimer
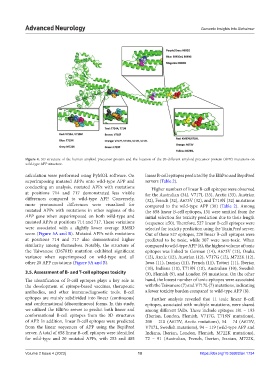
Figure 4. 3D structure of the human amyloid precursor protein and the location of the 20 different amyloid precursor protein (APP) mutations on
wild-type APP structure.
calculation were performed using PyMOL software. On linear B-cell epitopes predicted by the ElliPro and BepiPred
superimposing mutated APPs onto wild-type APP and servers (Table 2).
conducting an analysis, mutated APPs with mutations Higher numbers of linear B-cell epitopes were observed
at positions 714 and 717 demonstrated less visible for the Australian (34), V717L (33), Arctic (33), Austrian
differences compared to wild-type APP. Conversely, (32), French (32), A673V (32), and T719N (32) mutations
more pronounced differences were visualized for compared to the wild-type APP (30) (Table 2). Among
mutated APPs with mutations in other regions of the the 658 linear B-cell epitopes, 131 were omitted from the
APP gene when superimposed on both wild-type and initial selection for toxicity prediction due to their length
mutated APPs at positions 714 and 717. These variations (sequence ≥50). Therefore, 527 linear B-cell epitopes were
were associated with a slightly lower average RMSD selected for toxicity prediction using the ToxinPred server.
score (Figure 5A and B). Mutated APPs with mutations Out of these 527 epitopes, 220 linear B-cell epitopes were
at positions 714 and 717 also demonstrated higher predicted to be toxic, while 307 were non-toxic. When
similarity among themselves. Notably, the structure of compared to wild-type APP (8), the highest volume of toxic
the Taiwanese (D678H) mutation exhibited significant epitopes was linked to German (14), A673V (13), Osaka
variance when superimposed on wild-type and all (12), Arctic (12), Austrian (12), V717G (12), M722K (12),
other 20 APP mutations (Figure 5A and B). Iowa (11), Iranian (11), French (11), Tottori (11), Iberian
(10), Indiana (10), T719N (10), Australian (10), Swedish
3.5. Assessment of B- and T-cell epitopes toxicity (9), Flemish (9), and London (9) mutations. On the other
The identification of B-cell epitopes plays a key role in hand, the lowest number of toxic epitopes were associated
the development of epitope-based vaccines, therapeutic with the Taiwanese (7) and V717L (7) mutations, indicating
antibodies, and other immunodiagnostic tools. B-cell a lower toxicity burden compared to wild-type APP (8).
epitopes are mainly subdivided into linear (continuous) Further analysis revealed that 11 toxic linear B-cell
and conformational (discontinuous) forms. In this study, epitopes, associated with multiple mutations, were shared
we utilized the ElliPro server to predict both linear and among different fADs. These include epitopes 181 – 193
conformational B-cell epitopes from the 3D structures (Iberian, London, Flemish, V717G, T719N mutations),
of APP. In addition, linear B-cell epitopes were predicted 200 – 210 (A673V, Arctic mutations), 54 – 74 (A673V,
from the linear sequences of APP using the BepiPred V717L, Swedish mutations), 94 – 119 (wild-type APP and
server. A total of 658 linear B-cell epitopes were identified Indiana, Iberian, London, Flemish, M722K mutations),
for wild-type and 20 mutated APPs, with 253 and 405 72 – 91 (Australian, French, Iberian, Iranian, M722K,
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1734