Page 56 - AN-2-4
P. 56
Advanced Neurology Genomic insights into Alzheimer
A
B
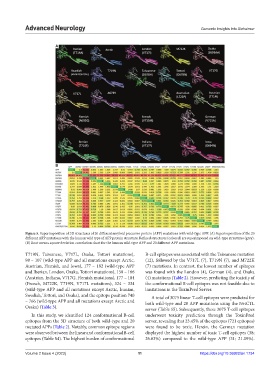
Figure 5. Superimposition of 3D structures of 20 different amyloid precursor protein (APP) mutations with wild-type APP. (A) Superimposition of the 20
different APP mutations with the human wild type of APP protein structure. Refined structures (colored) are superimposed on wild-type structures (grey).
(B) Root means square deviation correlation chart for the human wild-type APP and 20 different APP mutations.
T719N, Taiwanese, V717L, Osaka, Tottori mutations), B-cell epitopes was associated with the Taiwanese mutation
98 – 107 (wild-type APP and all mutations except Arctic, (12), followed by the V717L (7), T719N (7), and M722K
Austrian, Flemish, and Iowa), 177 – 182 (wild-type APP (7) mutations. In contrast, the lowest number of epitopes
and Iberian, London, Osaka, Tottori mutations), 158 – 166 was found with the London (4), German (4), and Osaka
(Austrian, Indiana, V717G, Flemish mutations), 177 – 184 (4) mutations (Table 2). However, predicting the toxicity of
(French, M722K, T719N, V717L mutations), 324 – 334 the conformational B-cell epitopes was not feasible due to
(wild-type APP and all mutations except Arctic, Iranian, limitations in the ToxinPred Server.
Swedish, Tottori, and Osaka), and the epitope position 740 A total of 3075 linear T-cell epitopes were predicted for
– 766 (wild-type APP and all mutations except Arctic and both wild-type and 20 APP mutations using the NetCTL
Osaka) (Table 3). server (Table S5). Subsequently, these 3075 T-cell epitopes
In this study, we identified 124 conformational B-cell underwent toxicity prediction through the ToxinPred
epitopes from the 3D structure of both wild-type and 20 server, revealing that 23.45% of the epitopes (721 epitopes)
mutated APPs (Table 2). Notably, common epitope regions were found to be toxic. Herein, the German mutation
were observed between the linear and conformational B-cell displayed the highest number of toxic T-cell epitopes (38;
epitopes (Table S4). The highest burden of conformational 26.03%) compared to the wild-type APP (31; 21.09%).
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1734