Page 93 - ARNM-2-3
P. 93
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Radiotherapy with neutron/gamma tubes
yield becomes 2 × 10 n/s and the average neutron yield is
11
2 × 10 n/s for 1% DF operation.
9
The beam target for the d-d neutron tube is a round
copper disk. It is coated with a thin layer of titanium on the
one side. Deuterium atoms are absorbed on the titanium
surface. Under ion beam bombardment, the temperature of
the target electrode will increase. If the temperature exceeds
250°C, most of the deuterium atoms will evaporate away.
The probability for the d-d fusion reaction to occur becomes
smaller. To maintain a high neutron yield, the target electrode
must be cooled by compressed air. For a 1 MV, 10 mA
D ion beam, the power density on the target electrode
−
2
with a diameter of 2 cm is about 3 kW/cm for continuous
operation. For 1% DF pulsed operation, the power density
2
is only 30 W/cm . Air cooling can easily maintain the target
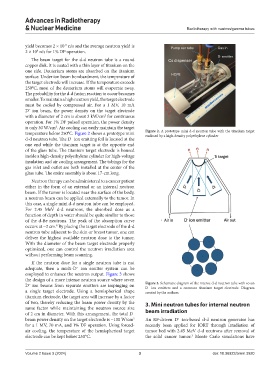
temperature below 250°C. Figure 2 shows a prototype mini Figure 2. A prototype mini d-d neutron tube with the titanium target
enclosed by a high-density polyethylene cylinder
d-d neutron tube. The D ion emitting foil is located at the
−
one end while the titanium target is at the opposite end
of the glass tube. The titanium target electrode is housed
inside a high-density polyethylene cylinder for high-voltage
insulation and air cooling arrangement. The tubings for the
gas inlet and outlet are both installed at the center of the
glass tube. The entire assembly is about 17-cm long.
Neutron therapy can be administered to a cancer patient
either in the form of an external or an internal neutron
beam. If the tumor is located near the surface of the body,
a neutron beam can be applied externally to the tumor. In
this case, a single mini d-d neutron tube can be employed.
For 2.45 MeV d-d neutrons, the absorbed dose as a
function of depth in water should be quite similar to those
of the d-Be neutrons. The peak of the absorption curve
occurs at ~2 cm. By placing the target electrode of the d-d
8
neutron tube adjacent to the skin or breast tumor, one can
deliver the highest available neutron dose to the tumor.
With the diameter of the beam target electrode properly
optimized, one can control the neutron irradiation area
without performing beam scanning.
If the neutron dose for a single neutron tube is not
adequate, then a multi-D ion emitter system can be
−
employed to enhance the neutron output. Figure 3 shows
the design of a more intense neutron source where seven
D ion beams from separate emitters are impinging on Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the intense d-d neutron tube with seven
−
D ion emitters and a common titanium target electrode. Diagram
−
a single target electrode. Using a hemispherical shape created by the authors.
titanium electrode, the target area will increase by a factor
of two, thereby reducing the beam power density by the 3. Mini neutron tubes for internal neutron
same factor while maintaining the neutron source size beam irradiation
of 2 cm in diameter. With this arrangement, the total D
−
beam power density on the target electrode is ~100 W/cm An RF-driven D ion-based d-d neutron generator has
2
+
for a 1 MV, 70 mA, and 1% DF operation. Using forced- recently been applied for IORT through irradiation of
air cooling, the temperature of the hemispherical target tumor bed with 2.45 MeV d-d neutrons after removal of
electrode can be kept below 250°C. the solid cancer tumor. Monte Carlo simulations have
3
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3920