Page 92 - ARNM-2-3
P. 92
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Radiotherapy with neutron/gamma tubes
these new findings, mini neutron/gamma-ray tubes are 2.45 MeV neutrons will be produced by the d-d fusion
now being developed which can eliminate most issues reaction. Titanium is used as the target material because
from the larger positive H /D ion-based neutron/gamma- it is capable of absorbing a large number of deuterium
+
+
ray generators. Using a high-frequency AC high-voltage atoms on the surface, thereby enabling more d-d reactions
supply, short pulses of high-intensity neutron or gamma- to occur and enhancing the neutron yield. Without an
ray beams can be generated using the d-d, d- B, d- Li, ion source chamber, the size of the neutron generator is
7
10
p- Li, or p- F nuclear reactions. This article describes significantly reduced. In addition, complex power sources
7
6
19
the design and development of these mini tubes and their such as an RF or microwave generator and its matching
applications for neutron or gamma-ray cancer therapy. network are eliminated, and a simple heater power supply
7
is all that is required to produce the H /D ion.
−
−
2. Mini neutron tube for external neutron
For low ion beam current, the neutron tube can be
beam therapy operated with a DC high voltage (~100 kV) power supply.
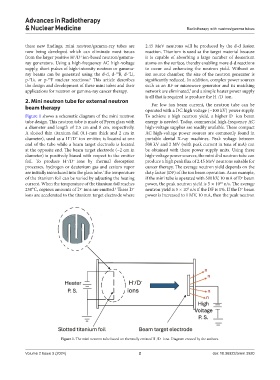
Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the mini neutron To achieve a high neutron yield, a higher D ion beam
−
tube design. This neutron tube is made of Pyrex glass with energy is needed. Today, commercial high-frequency AC
a diameter and length of 2.5 cm and 8 cm, respectively. high-voltage supplies are readily available. These compact
A slotted thin titanium foil (0.1-mm thick and 2 cm in AC high-voltage power sources are commonly found in
diameter), used as a H /D ion emitter, is located at one portable dental X-ray machines. Peak voltage between
−
−
end of the tube while a beam target electrode is located 500 kV and 2 MV (with peak current in tens of mA) can
at the opposite end. The beam target electrode (~2 cm in be obtained with these power supply units. Using these
diameter) is positively biased with respect to the emitter high-voltage power sources, the mini d-d neutron tube can
foil. To produce H /D ions by thermal desorption produce a high peak flux of 2.45 MeV neutrons suitable for
−
−
processes, hydrogen or deuterium gas and cesium vapor cancer therapy. The average neutron yield depends on the
are initially introduced into the glass tube. The temperature duty factor (DF) of the ion beam operation. As an example,
of the titanium foil can be varied by adjusting the heating if the mini tube is operated with 500 kV, 10 mA of D beam
−
current. When the temperature of the titanium foil reaches power, the peak neutron yield is 5 × 10 n/s. The average
10
250°C, copious amounts of D ions are emitted. These D neutron yield is 5 × 10 n/s if the DF is 1%. If the D beam
8
5
−
−
−
ions are accelerated to the titanium target electrode where power is increased to 1 MV, 10 mA, then the peak neutron
Figure 1. The mini neutron tube based on thermally emitted H /D ions. Diagram created by the authors.
−
−
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3920