Page 47 - ARNM-2-4
P. 47
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Outcomes of durations in 2D and 3D BT for CCA
A B C
D E F
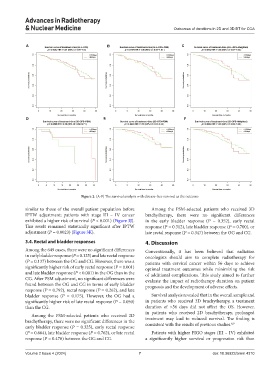
Figure 2. (A-F) The survival analysis with disease-free survival as the outcome
similar to those of the overall patient population before Among the PSM-selected patients who received 3D
IPTW adjustment; patients with stage III – IV cancer brachytherapy, there were no significant differences
exhibited a higher risk of survival (P < 0.001) (Figure 3J). in the early bladder response (P = 0.352), early rectal
This result remained statistically significant after IPTW response (P = 0.312), late bladder response (P = 0.700), or
adjustment (P = 0.0023) (Figure 3K). late rectal response (P = 0.347) between the OG and CG.
3.4. Rectal and bladder responses 4. Discussion
Among the 649 cases, there were no significant differences Conventionally, it has been believed that radiation
in early bladder response (P = 0.125) and late rectal response oncologists should aim to complete radiotherapy for
(P = 0.137) between the OG and CG. However, there was a patients with cervical cancer within 56 days to achieve
significantly higher risk of early rectal response (P = 0.001) optimal treatment outcomes while minimizing the risk
and late bladder response (P < 0.001) in the OG than in the of additional complications. This study aimed to further
CG. After PSM adjustment, no significant differences were evaluate the impact of radiotherapy duration on patient
found between the OG and CG in terms of early bladder prognosis and the development of adverse effects.
response (P = 0.792), rectal response (P = 0.262), and late
bladder response (P = 0.175). However, the OG had a Survival analysis revealed that in the overall sample and
significantly higher risk of late rectal response (P = 0.050) in patients who received 3D brachytherapy, a treatment
than the CG. duration of >56 days did not affect the OS. However,
in patients who received 2D brachytherapy, prolonged
Among the PSM-selected patients who received 2D
brachytherapy, there were no significant differences in the treatment may lead to reduced survival. The finding is
6,9
early bladder response (P = 0.325), early rectal response consistent with the results of previous studies.
(P = 0.664), late bladder response (P = 0.762), or late rectal Patients with higher FIGO stages (III – IV) exhibited
response (P = 0.470) between the OG and CG. a significantly higher survival or progression risk than
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4310