Page 48 - ARNM-2-4
P. 48
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Outcomes of durations in 2D and 3D BT for CCA
A B C D
E F G H
I K
J
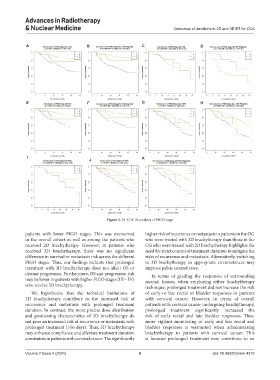
Figure 3. (A-K) K-M analysis of FIGO stage
patients with lower FIGO stages. This was overserved higher risk of recurrence or metastasis in patients in the OG
in the overall cohort as well as among the patients who who were treated with 2D brachytherapy than those in the
received 2D brachytherapy. However, in patients who CG who were treated with 2D brachytherapy highlights the
received 3D brachytherapy, there was no significant need for strict control of treatment duration to mitigate the
difference in survival or metastasis risk across the different risks of recurrence and metastasis. Alternatively, switching
FIGO stages. Thus, our findings indicate that prolonged to 3D brachytherapy in appropriate circumstances may
treatment with 3D brachytherapy does not affect OS or improve pelvic control rates.
disease progression. Furthermore, OS and progression risk In terms of grading the responses of surrounding
may be lower in patients with higher FIGO stages (III – IV) normal tissues, when employing either brachytherapy
who receive 3D brachytherapy. technique, prolonged treatment did not increase the risk
We hypothesize that the technical limitations of of early or late rectal or bladder responses in patients
2D brachytherapy contribute to the increased risk of with cervical cancer. However, in terms of overall
recurrence and metastasis with prolonged treatment patients with cervical cancer undergoing brachytherapy,
duration. In contrast, the more precise dose distribution prolonged treatment significantly increased the
and positioning characteristics of 3D brachytherapy do risk of early rectal and late bladder responses. Thus,
not pose an increased risk of recurrence or metastasis with more vigilant monitoring of early and late rectal and
prolonged treatment (>56 days). Thus, 3D brachytherapy bladder responses is warranted when administering
may enhance compliance and alleviate treatment duration brachytherapy to patients with cervical cancer. This
constraints in patients with cervical cancer. The significantly is because prolonged treatment may contribute to an
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4310