Page 76 - ARNM-2-4
P. 76
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Comparison of online ATP versus offline ATS plans
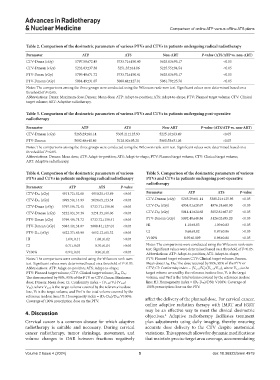
Table 2. Comparison of the dosimetric parameters of various PTVs and CTVs in patients undergoing radical radiotherapy
Parameter ATP ATS Non‑ART P‑value (ATS/ATP vs. non‑ART)
CTV-Dmax (cGy) 5797.59±72.45 5733.71±150.40 5625.63±95.17 <0.05
CTV-Dmean (cGy) 5232.03±37.38 5251.35±61.06 5225.55±94.54 <0.05
PTV-Dmax (cGy) 5799.49±71.72 5733.72±150.41 5625.63±95.17 <0.05
PTV-Dmean (cGy) 5084.49±31.07 5088.44±127.01 5061.79±25.76 <0.05
Notes: The comparisons among the three groups were conducted using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Significant values were determined based on a
threshold of P<0.05.
Abbreviations: Dmax: Maximum dose; Dmean: Mean dose; ATP: Adapt-to-position; ATS: Adapt-to-shape; PTV: Planned target volume; CTV: Clinical
target volume; ART: Adaptive radiotherapy.
Table 3. Comparison of the dosimetric parameters of various PTVs and CTVs in patients undergoing post‑operative
radiotherapy
Parameter ATP ATS Non‑ART P‑value (ATS/ATP vs. non‑ART)
CTV-Dmean (cGy) 5265.29±61.14 5305.21±125.93 5225.10±63.49 <0.05
PTV-Dmean 5092.40±40.86 5126.02±95.20 5060.55±51.03 <0.05
Notes: The comparisons among the three groups were conducted using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Significant values were determined based on a
threshold of P<0.05.
Abbreviations: Dmean: Mean dose; ATP: Adapt-to-position; ATS: Adapt-to-shape; PTV: Planned target volume; CTV: Clinical target volume;
ART: Adaptive radiotherapy.
Table 4. Comparison of the dosimetric parameters of various Table 5. Comparison of the dosimetric parameters of various
PTVs and CTVs in patients undergoing radical radiotherapy PTVs and CTVs in patients undergoing post‑operative
radiotherapy
Parameter ATP ATS P‑value
CTV-D98 (cGy) 4911.72±52.66 4950.25±43.89 <0.05 Parameter ATP ATS P‑value
CTV-D95 (cGy) 4995.50±14.99 5024.65±23.34 <0.05 CTV-Dmean (cGy) 5265.29±61.14 5305.21±125.93 <0.05
CTV-Dmax (cGy) 5797.59±72.45 5733.71±150.40 <0.05 CTV-D98 (cGy) 4934.01±28.67 4976.18±60.90 <0.05
CTV-Dmean (cGy) 5232.03±37.38 5251.35±61.06 <0.05 CTV-D95 (cGy) 5014.41±24.68 5052.61±67.87 <0.05
PTV-Dmax (cGy) 5799.49±71.72 5733.72±150.41 <0.05 PTV-Dmean (cGy) 5092.40±40.86 5126.02±95.20 <0.05
PTV-Dmean (cGy) 5084.49±31.07 5088.44±127.01 <0.05 HI 1.10±0.03 1.09±0.03 >0.05
PTV-D95 (cGy) 4622.37±45.98 4652.12±65.32 <0.05 CI 0.68±0.02 0.67±0.06 >0.05
HI 1.09±0.11 1.08±0.02 >0.05 V100% 0.95±0.009 0.96±0.01 <0.05
CI 0.71±0.03 0.70±0.04 >0.05 Notes: The comparisons were conducted using the Wilcoxon rank-sum
test. Significant values were determined based on a threshold of P<0.05.
V100% 0.94±0.01 0.96±0.01 <0.05 Abbreviations: ATP: Adapt-to-position; ATS: Adapt-to-shape;
Notes: The comparisons were conducted using the Wilcoxon rank-sum PTV: Planned target volume; CTV: Clinical target volume; Dmean,
test. Significant values were determined based on a threshold of P<0.05. Mean dose; D98, D95: The dose received by 98%, 95% of the PTV or
Abbreviations: ATP: Adapt-to-position; ATS: Adapt-to-shape; CTV; CI: Conformity index = (Vt, ref/Vt)·(Vt, ref/Vref), where Vt, ref is the
PTV: Planned target volume; CTV: Clinical target volume; D98, D95: target volume covered by the reference isodose line, Vt is the target
The dose received by 98%, 95% of the PTV or CTV; Dmax: Maximum volume, and Vref is the total volume covered by the reference isodose
dose; Dmean: Mean dose; CI: Conformity index = (Vt, ref/Vt)·(Vt, ref/ line; HI: Homogeneity index = (D2-D98)/D50; V100%: Coverage of
Vref), where Vt, ref is the target volume covered by the reference isodose 100% prescription dose on the PTV.
line, Vt is the target volume, and Vref is the total volume covered by the
reference isodose line; HI: Homogeneity index = (D2-D98)/D50; V100%:
Coverage of 100% prescription dose on the PTV. affect the delivery of the planned dose. For cervical cancer,
online adaptive radiation therapy with IMRT and IGRT
4. Discussion may be an effective way to meet the clinical dosimetric
objectives. Adaptive radiotherapy facilitates treatment
2
Cervical cancer is a common disease for which adaptive plan adjustments using daily imaging, thereby ensuring
radiotherapy is suitable and necessary. During cervical accurate dose delivery to the CTV despite anatomical
cancer radiotherapy, tumor shrinkage, movement, and variations. This approach allows for dynamic modifications
volume changes in OAR between fractions negatively that maintain precise target area coverage, accommodating
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4919