Page 75 - ARNM-3-1
P. 75
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Aspirin’s protective effect on RISI
A
B C D
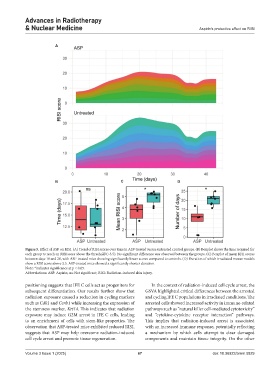
Figure 5. Effect of ASP on RISI. (A) Trend of RISI scores over time in ASP-treated versus untreated control groups. (B) Boxplot shows the time required for
each group to reach an RISI score above the threshold (>3.5). No significant difference was observed between the groups. (C) Boxplot of mean RISI scores
between days 18 and 20, with ASP-treated mice showing significantly lower scores compared to controls. (D) Duration of which irradiated mouse models
show a RISI score above 3.5. ASP-treated mice showed a significantly shorter duration.
Note: *indicates significance at p < 0.05.
Abbreviations: ASP: Aspirin; ns: Not significant; RISI: Radiation-induced skin injury.
positioning suggests that IFE C cells act as progenitors for In the context of radiation-induced cell cycle arrest, the
subsequent differentiation. Our results further show that GSVA highlighted critical differences between the arrested
radiation exposure caused a reduction in cycling markers and cycling IFE C populations in irradiated conditions. The
such as Cdk1 and Ccnb1 while increasing the expression of arrested cells showed increased activity in immune-related
the stemness marker, Krt14. This indicates that radiation pathways such as “natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity”
exposure may induce G2M arrest in IFE C cells, leading and “cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction” pathways.
to an enrichment of cells with stem-like properties. The This implies that radiation-induced arrest is associated
observation that ASP-treated mice exhibited reduced RISI, with an increased immune response, potentially reflecting
suggests that ASP may help overcome radiation-induced a mechanism by which cells attempt to clear damaged
cell cycle arrest and promote tissue regeneration. components and maintain tissue integrity. On the other
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 67 doi: 10.36922/arnm.5829