Page 46 - BH-2-2
P. 46
Brain & Heart VR for TBI memory and eye fixation recovery
Table 3. Percentage of time participants were able to intervention and delayed-intervention groups is needed
successfully fixate their eyes in the eye‑tracking virtual to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of these VR
reality scenario scenarios. Future research on these scenarios will include
Session M (standard deviation) individuals with TBI with acute injuries to assess its
Initial 75% (16%) feasibility, acceptability, and effects on newer injuries and
outcomes.
Middle 75% (22%)
Last 92% (7%) Both the VR scenarios demonstrated promise for
improving prospective memory and eye tracking
among individuals with TBI. Future research should
assess their effects on larger sample sizes to assess their
efficacy. VR should be considered as a rehabilitative
option for cognitive and vision recovery among
individuals with TBI.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Lily
Zepeda at the Brain Injury Center of Ventura County for
helping with scheduling recruitment opportunities.
Funding
Research, Scholarly, and Creative Award from California
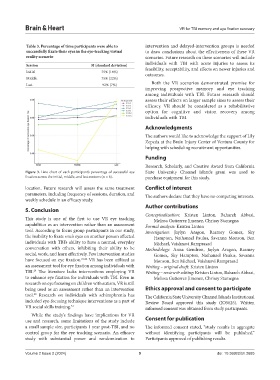
Figure 3. Line chart of each participant’s percentage of successful eye State University Channel Islands grant was used to
fixation across the initial, middle, and last sessions (n = 6). purchase equipment for this study.
location. Future research will assess the same treatment Conflict of interest
parameters, including frequency of sessions, duration, and The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
weekly schedule in an efficacy study.
Author contributions
5. Conclusion
Conceptualization: Kristen Linton, Bahareh Abbasi,
This study is one of the first to use VR eye tracking Melissa Gutierrez Jimenez, Chrissy Stamegna
capabilities as an intervention rather than an assessment Formal analysis: Kristen Linton
tool. According to focus group participants in our study, Investigation: Jaylyn Aragon, Rasmey Gomez, Sky
the inability to fixate one’s eyes on another person affected Hampton, Nathanael Paulus, Savanna Monson, Ben
individuals with TBI’s ability to have a normal, everyday Michael, Vaishnavi Ramprasad
conversation with others, inhibiting their ability to be Methodology: Anna Gendron, Jaylyn Aragon, Rasmey
social, work, and learn effectively. Few intervention studies Gomez, Sky Hampton, Nathanael Paulus, Savanna
have focused on eye fixation. 21,22 VR has been utilized as Monson, Ben Michael, Vaishnavi Ramprasad
an assessment tool for eye fixation among individuals with Writing – original draft: Kristen Linton
TBI. The literature lacks interventions employing VR Writing – review & editing: Kristen Linton, Bahareh Abbasi,
29
to enhance eye fixation for individuals with TBI. Even in Melissa Gutierrez Jimenez, Chrissy Stamegna
research on eye focusing on children with autism, VR is still
being used as an assessment rather than an intervention Ethics approval and consent to participate
tool. Research on individuals with schizophrenia has The California State University Channel Islands Institutional
30
included eye-focusing technique interventions as a part of Review Board approved this study (IO5625). Written
VR social skills training. 31 informed consent was obtained from study participants.
While the study’s findings have implications for VR
use and research, some limitations of the study include Consent for publication
a small sample size, participants 1 year post-TBI, and no The informed consent stated, “study results in aggregate
control group for the eye tracking scenario. An efficacy without identifying participants will be published.”
study with substantial power and randomization to Participants approved of publishing results.
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/bh.2685