Page 63 - EER-2-3
P. 63
Explora: Environment
and Resource Electrocatalyst for ammonia oxidation reaction
A B
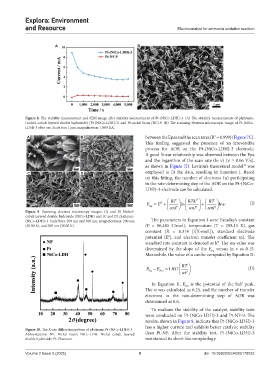
Figure 8. The stability measurement and SEM image after stability measurement of Pt-(NiCo-LDH)-3. (A) The stability measurements of platinum–
(nickel–cobalt layered double hydroxide) (Pt-[NiCo-LDH]-3) and Pt-nickel foam (NF)-9. (B) The scanning electron microscopic image of Pt-(NiCo-
LDH)-3 after use. Scale bar: 1 μm, magnification: 10.00 KX.
A B between the Epas and the scan rates (R = 0.999) (Figure 7C).
2
This finding suggested the presence of an irreversible
process for AOR on the Pt-(NiCo-LDH)-3 electrode.
A good linear relationship was observed between the Epa
and the logarithm of the scan rate (ln ν) (ν ≥ 0.06 V/s),
as shown in Figure 7D. Laviron’s theoretical model was
29
C D employed to fit the data, resulting in Equation I. Based
on this fitting, the number of electrons (n) participating
in the rate-determining step of the AOR on the Pt-(NiCo-
LDH)-3 electrode can be calculated.
RT θ RTk RT
E Pa = E θ + ln + ln ν (I)
Figure 9. Scanning electron microscopy images. (A and B) Nickel– α αnF αnF nF
cobalt layered double hydroxide (NiCo-LDH) and (C and D) platinum-
(NiCo-LDH)-3. Scale bars: 200 nm and 500 nm, magnifications: 200 nm The parameters in Equation I were Faraday’s constant
(50.00 K), and 500 nm (20.00 K). (F = 96,485 C/mol), temperature (T = 298.15 K), gas
constant (R = 8.314 J/[K·moL]), standard electrode
potential (E ), and electron transfer coefficient (α). The
θ
standard rate constant is denoted as k . The αn value was
θ
determined by the slope of the E versus ln ν as 0.15.
Pa
Meanwhile, the value of α can be computed by Equation II:
RT
− E = E 1.857 (II)
Pa P /2
α F
In Equation II, E is the potential of the half peak.
P∕2
The α was calculated as 0.25, and the number of transfer
electrons in the rate-determining step of AOR was
determined as 0.6.
To evaluate the stability of the catalyst, stability tests
were conducted on Pt-(NiCo-LDH)-3 and Pt-NF-9. The
results, shown in Figure 8, indicate that Pt-(NiCo-LDH)-3
has a higher current and exhibits better catalytic stability
Figure 10. The X-ray diffraction pattern of platinum Pt-(NiCo-LDH)-3
Abbreviations: NF: Nickel foam; NiCo-LDH: Nickel–cobalt layered than Pt-NF. After the stability test, Pt-(NiCo-LDH)-3
double hydroxide; Pt: Platinum. maintained its sheet-like morphology.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/EER025170033