Page 224 - EJMO-9-3
P. 224
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology FN3K–Nrf2 axis inhibition in breast cancer
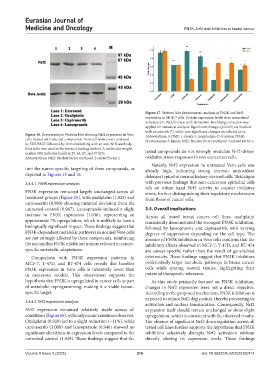
Figure 17. Western blot densitometric analysis of FN3K and Nrf2
expression in MCF-7 cells. Protein expression levels were normalized
to beta actin. Welch’s t-test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction was
applied for statistical analysis. Significant changes (p<0.05) are marked
with an asterisk (*), while non-significant changes are labeled as ns
Figure 16. Representative Western blot showing Nrf2 expression in Vero Abbreviations: 1-DMF: 1-deoxy-1-morpholino-D-fructose; FN3K:
cells treated with selected compounds. Vero cell lysates were analyzed Fructosamine-3-kinase; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with an anti-Nrf2 antibody.
Beta actin was used as the internal loading control. A molecular weight
marker (M) indicates bands at 29, 45, 67, and 97 kDa tested compounds do not strongly modulate Nrf2-driven
Abbreviations: Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 oxidative stress responses in non-cancerous cells.
Notably, Nrf2 expression in untreated Vero cells was
into the tumor-specific targeting of these compounds, as already high, indicating strong intrinsic antioxidant
depicted in Figures 15 and 16. defenses typical of normal kidney-derived cells. This aligns
3.4.4.1. FN3K expression analysis with previous findings that non-cancerous epithelial cells
rely on robust basal Nrf2 activity to counter oxidative
FN3K expression remained largely unchanged across all stress, further distinguishing their regulatory mechanisms
treatment groups (Figure 15), with oxaliplatin (1.024) and from those of cancer cells.
capivasertib (0.980) showing minimal deviation from the
untreated control (0.967). Lansoprazole induced a slight 3.5. Overall implications
increase in FN3K expression (1.036), representing an Across all tested breast cancer cell lines, oxaliplatin
approximate 7% upregulation, which is unlikely to have a consistently demonstrated the strongest FN3K inhibition,
biologically significant impact. These findings suggest that followed by lansoprazole and capivasertib, with varying
FN3K-dependent metabolic pathways in normal Vero cells degrees of suppression depending on the cell type. The
are not strongly affected by these compounds, reinforcing absence of FN3K inhibition in Vero cells confirms that the
the notion that FN3K inhibition is more relevant in cancer- inhibitory effects observed in MCF-7, T-47D, and BT-474
specific metabolic adaptations. are cancer-specific rather than the result of generalized
Comparison with FN3K expression patterns in cytotoxicity. These findings suggest that FN3K inhibitors
MCF-7, T-47D, and BT-474 cells reveals that baseline preferentially target metabolic pathways in breast cancer
FN3K expression in Vero cells is inherently lower than cells while sparing normal tissues, highlighting their
in cancerous models. This observation supports the potential therapeutic relevance.
hypothesis that FN3K is upregulated in cancer cells as part As this study primarily focused on FN3K inhibition,
of metabolic reprogramming, making it a viable tumor- changes in Nrf2 expression were not a direct objective.
specific target. According to the proposed mechanism, FN3K inhibition is
expected to reduce Nrf2 deglycation, thereby preventing its
3.4.4.2. Nrf2 expression analysis
activation and nuclear translocation. Consequently, Nrf2
Nrf2 expression remained relatively stable across all expression itself should remain unchanged or show slight
conditions (Figure 16), with only minor variations observed. upregulation, which is consistent with the observed results.
Oxaliplatin (0.929) led to a slight reduction (~11%), while The absence of significant Nrf2 downregulation across all
capivasertib (1.008) and lansoprazole (0.946) showed no tested cell lines further supports the hypothesis that FN3K
significant alterations in expression levels compared to the inhibition selectively disrupts Nrf2 activation without
untreated control (1.049). These findings suggest that the directly altering its expression levels. These findings
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 216 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025150114