Page 279 - EJMO-9-3
P. 279
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology WGCNA and LASSO for osteoporosis biomarkers
A B C
D E
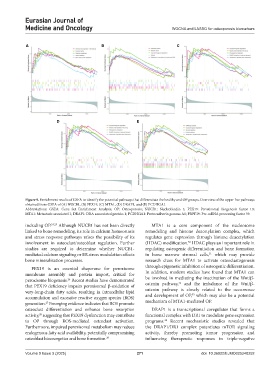
Figure 9. Enrichment results of GSEA to identify the potential pathways that differentiate the healthy and OP groups. Overview of the upper five pathways
obtained from GSEA of (A) NUCB1, (B) PEX19, (C) MTA1, (D) DRAP1, and (E) PCDHGA1.
Abbreviations: GSEA: Gene Set Enrichment Analysis; OP: Osteoporosis; NUCB1: Nucleobindin 1; PEX19: Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 19;
MTA1: Metastasis associated 1; DRAP1: DRA aassociated protein 1; PCDHGA1: Protocadherin gamma A1; PRPF39: Pre-mRNA processing factor 39.
including OP. 24,25 Although NUCB1 has not been directly MTA1 is a core component of the nucleosome
linked to bone remodeling, its role in calcium homeostasis remodeling and histone deacetylation complex, which
and stress response pathways raises the possibility of its regulates gene expression through histone deacetylation
involvement in osteoclast/osteoblast regulation. Further (HDAC) modification. HDAC plays an important role in
30
studies are required to determine whether NUCB1- regulating osteogenic differentiation and bone formation
mediated calcium signaling or ER stress modulation affects in bone marrow stromal cells, which may provide
31
bone mineralization processes. research clues for MTA1 to activate osteoclastogenesis
PEX19 is an essential chaperone for peroxisome through epigenetic inhibition of osteogenic differentiation.
membrane assembly and protein import, critical for In addition, modern studies have found that MTA1 can
peroxisome biogenesis. Recent studies have demonstrated be involved in mediating the inactivation of the Wnt/β-
26
32
that PEX19 deficiency impairs peroxisomal β-oxidation of catenin pathway, and the imbalance of the Wnt/β-
very-long-chain fatty acids, resulting in intracellular lipid catenin pathway is closely related to the occurrence
33
accumulation and excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and development of OP, which may also be a potential
27
generation. Emerging evidence indicates that ROS promote mechanism of MTA1-mediated OP.
osteoclast differentiation and enhance bone resorption DRAP1 is a transcriptional coregulator that forms a
activity, suggesting that PEX19 dysfunction may contribute functional complex with DR1 to modulate gene expression
28
to OP through ROS-mediated osteoclast activation. programs. Recent mechanistic studies revealed that
34
Furthermore, impaired peroxisomal metabolism may reduce the DRAP1/DR1 complex potentiates mTOR signaling
endogenous fatty acid availability, potentially compromising activity, thereby promoting tumor progression and
osteoblast bioenergetics and bone formation. 29 influencing therapeutic responses in triple-negative
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 271 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025240252